Circulating metabolic biomarkers predict incident sepsis: a large-scale population study in the UK Biobank
- PMID: 40817246
- PMCID: PMC12357410
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-025-01191-9
Circulating metabolic biomarkers predict incident sepsis: a large-scale population study in the UK Biobank
Abstract
Background: Currently, there is an absence of large-scale research focusing on the metabolome profiles of individuals prior to the development of sepsis. This study aimed to evaluate the associations of circulating Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) metabolic biomarkers with the risk of incident sepsis and the predictive ability of these metabolites for sepsis.
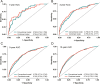
Methods: The analysis utilized plasma metabolomic data measuring through NMR from the UK Biobank, which involved baseline plasma samples of 106,533 participants. The multivariable-adjusted Cox proportional hazard models were used to assess the associations of each circulating NMR metabolite biomarker with risk of incident sepsis. The full cohort was randomly assigned to a training set (n = 53,267) and a test set (n = 53,266) to develop and validate the sepsis risk prediction model. In training set, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and stepwise Cox regression analyses were used to develop the prediction model. In test set, the predictive ability of conventional risk factors-based and combined metabolic biomarkers prediction model was assessed by Harrell's C-index. The incremental predictive power of the metabolic biomarkers was evaluated with continuous net reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
Results: A total of 90 circulating metabolic biomarkers were significantly associated with risk of incident sepsis (all FDR adjusted P value < 0.05). Of these, triglycerides related lipid sub-classes, glycolysis, ketone bodies, and inflammation related metabolite biomarkers, creatinine, and phenylalanine were positively associated with risk of incident sepsis, while most of other lipid sub-classes, albumin, histidine, fatty acid and cholines related metabolic biomarkers were negatively associated with risk of sepsis. The Harrell's C-index of the conventional prediction model was 0.733 (95% CI: 0.722, 0.745) for incident sepsis; after adding the circulating NMR metabolic biomarkers to the conventional prediction model, the Harrell's C-index increased to 0.741 (95% CI: 0.730, 0.753) for incident sepsis. In addition, the continuous NRI and IDI were 0.022 (95% CI: 0.015, 0.043, P < 0.05) and 0.009 (95% CI: 0.006, 0.014, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study identified multiple plasma metabolic biomarkers were associated with risk of incident sepsis. The addition of these metabolic biomarkers to the conventional risk factors-based model significantly improved the prediction precision.
Keywords: Metabolic biomarkers; Sepsis; UK biobank.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triglyceride-glucose-related indices and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in individuals with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome stages 0-3: a prospective cohort study of 282,920 participants in the UK Biobank.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02842-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40640813 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of different insulin resistance-related indices with the incidence and progression trajectory of cardiometabolic multimorbidity: a prospective cohort study from UK biobank.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jun 18;24(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02819-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40533754 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism-related inflammatory indices (LMIIs) and incident peripheral artery diseases (PAD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): a multicohort study from China and the UK biobank.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 22;24(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02887-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40847315 Free PMC article.
-
The comparative and added prognostic value of biomarkers to the Revised Cardiac Risk Index for preoperative prediction of major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality in patients who undergo noncardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 21;12(12):CD013139. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013139.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34931303 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Levy MM, Evans LE, Rhodes A. The surviving sepsis campaign bundle: 2018 update. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44:925–8. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, Machado FR, Angus DC, Calandra T, Jaton K, Giulieri S, Delaloye J, Opal S, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:581–614. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

