The fibrosis puzzle of systemic sclerosis-associated ILD and the quest for targeted interventions
- PMID: 40817801
- PMCID: PMC12358001
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666251366023
The fibrosis puzzle of systemic sclerosis-associated ILD and the quest for targeted interventions
Abstract
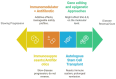
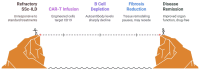
Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in systemic sclerosis, marked by complex immunopathogenic mechanisms and progressive fibrosis. Recent advances have illuminated key cellular players as T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and profibrotic mediators such as TGF-β, PDGF, and CTGF, alongside emerging roles for epigenetic reprogramming in sustaining fibroblast activation. This narrative review synthesizes current understanding of immune-fibrotic crosstalk and critically evaluates both established therapies (e.g., mycophenolate mofetil, nintedanib, tocilizumab, and rituximab) and novel targeted approaches. Particular attention is given to emerging immunomodulatory, antifibrotic, and cell-based therapies, including CAR-T and mesenchymal stem cell treatments, as well as the potential of epigenetic modulators repurposed from oncology. By bridging basic science and clinical practice, this review outlines the evolving therapeutic landscape of SSc-ILD and highlights opportunities for future research and personalized intervention.
Keywords: CAR-T; epigenetics; fibrosis; immunopathogenesis; interstitial lung disease; mycophenolate mofetil; nintedanib; systemic sclerosis; targeted therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Fedorchenko Y, Zimba O, Yatsyshyn R, et al. The interplay between rheumatic diseases and pulmonary health. Rheumatol Int 2024; 44: 1179–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

