Adipose-Derived Exosomes: mediators of crosstalk between Adipose tissue and cancer
- PMID: 40817844
- PMCID: PMC12360202
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2547564
Adipose-Derived Exosomes: mediators of crosstalk between Adipose tissue and cancer
Abstract
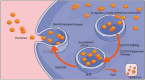
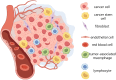
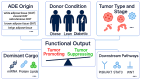
Adipose-derived exosomes (ADEs), a subtype of extracellular vesicles, are critical mediators of communication between adipose tissue and tumors, playing pivotal roles in cancer progression and therapeutic response. These nanoscale vesicles carry microRNAs, proteins, and lipids that influence tumor cell proliferation, migration, metastasis, and immune modulation. The dual functions of ADEs - both in promoting and suppressing tumorigenesis - are largely dependent on their cellular origin, molecular cargo, and the characteristics of the tumor microenvironment. Recent studies have identified ADEs as potential diagnostic biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and drug delivery platforms, offering promising avenues for precision oncology. However, significant challenges - such as biological heterogeneity, lack of standardization in production, concerns regarding efficacy and safety, and regulatory constraints - continue to hinder their clinical translation. This review aimed to explore the multifaceted roles of ADEs in cancer pathogenesis, their therapeutic potential, and current limitations, providing insights to guide future research and clinical applications.
Keywords: Adipose-derived exosomes; adipose tissue; cancer; exosome-based therapy; miRNA; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Role of Exosome in Solid Cancer Progression and Its Potential Therapeutics in Cancer Treatment.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(9):e70941. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70941. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40344389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: a potential tool in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of patients with colorectal cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug;21(18):2347-2365. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2520150. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40515703 Review.
-
[Research progress of peptide recognition-guided strategies for exosome isolation and enrichment].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):446-454. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.10015. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331609 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Engineering exosomes for liver disease: a new insight in regenerative medicine and drug delivery.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 3. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05309-x. Online ahead of print. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40608260 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
