PTK6 mediated immune signatures revealed by single cell transcriptomic and multi omics big data analysis in cervical cancer
- PMID: 40818002
- PMCID: PMC12357816
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03365-7
PTK6 mediated immune signatures revealed by single cell transcriptomic and multi omics big data analysis in cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer exhibits heterogeneous clinical outcomes, requiring improved prognostic tools. Single-cell RNA sequencing enables high-resolution analysis of tumor microenvironment cellular heterogeneity. This study developed a prognostic model for cervical cancer through single-cell transcriptomic analysis and immune infiltration characterization, focusing on PTK6 as a key biomarker.
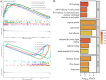
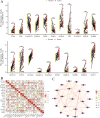
Methods: We analyzed TCGA and GEO transcriptomic data with single-cell RNA sequencing datasets. Fifteen machine learning algorithms constructed prognostic models using immune infiltration-related genes. Single-cell analysis employed Seurat for cell clustering and annotation. PTK6 expression was validated in H8 and HeLa cell lines via RT-qPCR and siRNA knockdown experiments.
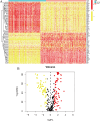
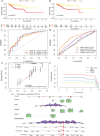
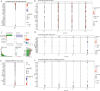
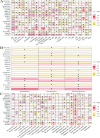
Results: Single-cell sequencing revealed distinct cellular populations including CD8T cells, CD4Tconv cells, and fibroblasts. The prognostic model achieved excellent performance with AUC values of 0.737-0.757 across 1-5 years. PTK6 showed significantly elevated expression in tumors and strong correlations with immune infiltration. Single-cell analysis confirmed PTK6 expression across multiple cell types. Functional validation demonstrated that PTK6 knockdown reduced HeLa cell proliferation, confirming its oncogenic role.
Conclusion: PTK6 emerges as a critical immune infiltration-related prognostic biomarker through single-cell transcriptomic analysis.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Immune infiltration; Machine learning; PTK6; Prognostic biomarker; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Not available. Consent to publish: All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Consent to participate: Not available. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics-based prognostic value and in vitro functional validation of PTK6 in cutaneous melanoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 30;15:1555302. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1555302. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40809015 Free PMC article.
-
SLC3A2 as a key anoikis-related gene for prognosis and tumor microenvironment remodeling in melanoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 11;16(1):1306. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03125-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40643718 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between tumor mutation burden and the tumor microenvironment predicts the prognosis of pan-cancer anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1557461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557461. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40777041 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel molecular subtypes and construction of a prognostic signature via multi-omics analysis and machine learning in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 21;15:1590216. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1590216. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40761262 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-gene anoikis signature combined with tumor microenvironment stratifies prognosis in cutaneous melanoma with experimental validation of PTK6.Gene. 2025 Jul 26;966:149686. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2025.149686. Online ahead of print. Gene. 2025. PMID: 40721013
References
-
- Shamsutdinova A, Kulkayeva G, Karashutova Z, Tanabayev B, Tanabayeva S, Ibrayeva A, Fakhradiyev I. Analysis of the effectiveness and coverage of breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer screening programs in Kazakhstan for the period 2021–2023: regional disparities and coverage dynamics. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024;25(12):4371–80. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Lu L, Xu C, Wang D, Zeng B, Liu M. Development and external validation of a multi-task feature fusion network for CTV segmentation in cervical cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 2024:110699. - PubMed
-
- Guo S, Jiang H, Deng Y, Dong Y, Yin A, Wang Q, Lan Q, Zhang Y, Xu C. Reduced 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase 1 is served as an unfavorable biomarker and is related to immune infiltration in cervical cancer. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2023;49(10):2475–86. - PubMed
