UPLC-Q-TOF/MS, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation to explore the mechanisms of toad clothing on rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40819108
- PMCID: PMC12357956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-16053-x
UPLC-Q-TOF/MS, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation to explore the mechanisms of toad clothing on rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
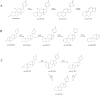
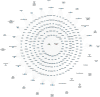
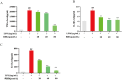
Toad clothing (toad slough) detoxifies, reduces oedema and analgesia, is anti-inflammatory and anti-tumour, and regulates the immune system. Toad clothing's mechanism is unclear. The molecular mechanism of toad clothing in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy will be investigated in this research. We used Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF/MS), network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vitro experiments to investigate the mechanism behind the anti-RA action of toad apparel. First, UPLC-Q-TOF/MS revealed 24 toad clothing ingredients. Network pharmacology predicted five key elements, six core targets, and the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/ Protein Kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signalling pathway. Then, molecular docking was used to validate the binding ability of core chemical constituents and core targets of toad clothing. The results showed that the primary constituent, resibufogenin, was bound tightly to six core targets and had a good affinity for key RA targets such as Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), and Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2). Cellular tests demonstrated that resibufogenin dramatically lowered Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) levels and regulated the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. This research showed toad clothing's anti-RA pharmacodynamic material basis and mechanism, offering a theoretical foundation for its creation, use, and clinical application.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








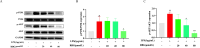
Similar articles
-
Sishen pill alleviates ulcerative colitis via the NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway: Comprehensive validation through UPLC-Q-TOF/MS, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vivo experiments.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025 Oct 1;1264:124735. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2025.124735. Epub 2025 Jul 13. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40675106
-
The Potential Mechanisms of Banxia Xiexin Decoction in Treating Chronic Colitis: Insights from UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and Network Pharmacology Studies.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.2174/0113862073350796250305225907. Online ahead of print. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 40662553
-
Uncovering the mechanisms of Zhubi decoction against rheumatoid arthritis through an integrated study of network pharmacology, metabolomics, and intestinal flora.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 10;336:118736. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118736. Epub 2024 Aug 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39186991
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
-
Study on the mechanism of Shujin Tongluo granules in treating cervical spondylosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 21;102(29):e34030. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034030. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37478234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Matteo, A., Bathon, J. M. & Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet402, 2019–2033 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Gravallese, E. M. et al. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?. N. Engl. J. Med.390, e32 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Gan, P.-R., Wu, H., Zhu, Y.-L., Shu, Y. & Wei, Y. Glycolysis, a driving force of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol.132, 111913 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- QKHJC-ZK [2023] -302/Guizhou Province Science and Technology Fund
- QZYY-2024-012/Special Project for Scientific and Technological Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ethnic Medicine of Guizhou Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 82401632/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

