Systems biology-enabled targeting of NF-κΒ and BCL2 overcomes microenvironment-mediated BH3-mimetic resistance in DLBCL
- PMID: 40819126
- PMCID: PMC12357900
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07942-0
Systems biology-enabled targeting of NF-κΒ and BCL2 overcomes microenvironment-mediated BH3-mimetic resistance in DLBCL
Abstract
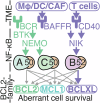
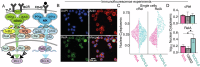
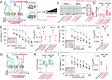
In Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), elevated anti-apoptotic BCL2-family proteins (e.g., MCL1, BCL2, BCLXL) and NF-κB subunits (RelA, RelB, cRel) confer poor prognosis. Heterogeneous expression, regulatory complexity, and redundancy offsetting the inhibition of individual proteins, complicate the assignment of targeted therapy. We combined flow cytometry 'fingerprinting', immunofluorescence imaging, and computational modeling to identify therapeutic vulnerabilities in DLBCL. The combined workflow predicted selective responses to BCL2 inhibition (venetoclax) and non-canonical NF-κB inhibition (Amgen16). Within the U2932 cell line we identified distinct resistance mechanisms to BCL2 inhibition in cellular sub-populations recapitulating intratumoral heterogeneity. Co-cultures with CD40L-expressing stromal cells, mimicking the tumor microenvironment (TME), induced resistance to BCL2 and BCLXL targeting BH3-mimetics via cell-type specific upregulation of BCLXL or MCL1. Computational models, validated experimentally, showed that basal NF-κB activation determined whether CD40 activation drove BH3-mimetic resistance through upregulation of RelB and BCLXL, or cRel and MCL1. High basal NF-κB activity could be overcome by inhibiting BTK to resensitize cells to BH3-mimetics in CD40L co-culture. Importantly, non-canonical NF-κB inhibition overcame heterogeneous compensatory BCL2 upregulation, restoring sensitivity to both BCL2- and BCLXL-targeting BH3-mimetics. Combined molecular fingerprinting and computational modelling provides a strategy for the precision use of BH3-mimetics and NF-κB inhibitors in DLBCL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS: YL is a shareholder of DeepKinase Biotechnologies. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Animal work was performed according to guidelines from the University of California, Los Angeles under approved ARC protocols (B-14-110 for breeding and R-14-126 for experiment).
Figures


Update of
-
Systems biology-enabled targeting of NF-κΒ and BCL2 overcomes microenvironment-mediated BH3-mimetic resistance in DLBCL.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 1:2024.11.30.626166. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.30.626166. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Death Dis. 2025 Aug 16;16(1):620. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07942-0. PMID: 39677808 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Davies A, Barrans S, Burton C, Mercer K, Caddy J, Chinnery F, et al. ACCEPT - combining acalabrutinib with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone (R-CHOP) for diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): study protocol for a Phase Ib/II open-label non-randomised clinical trial. F1000Res. 2020;9:941. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feugier P, Hoof AV, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Fermé C, et al. Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4117–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

