Risk factors and nomogram prediction model for pneumothorax after CT-guided coaxial biopsy combined with microwave ablation in ground-glass nodules
- PMID: 40819621
- PMCID: PMC12390949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100750
Risk factors and nomogram prediction model for pneumothorax after CT-guided coaxial biopsy combined with microwave ablation in ground-glass nodules
Abstract
Objective: To identify risk factors and develop a validated nomogram for predicting pneumothorax after CT-guided coaxial biopsy with synchronous Microwave Ablation (MWA) in Ground-Glass Nodules (GGNs).
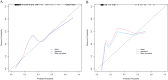
Methods: 383 GGN patients were divided into a training set (n = 268) and a validation set (n = 115) in a 7:3 ratio. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were employed to identify risk factors, followed by the construction of a nomogram model. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves and calibration plots were generated to evaluate model performance, with further validation in the independent cohort. Decision curve analysis was applied to assess clinical utility.
Results: Pneumothorax occurred in 72 cases (26.87 %) in the training set and 32 cases (27.83 %) in the validation set. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that BMI, lesion location, lesion depth, needle diameter, and number of punctures were independent risk factors for pneumothorax (all p < 0.05). Factor importance ranking was as follows: number of punctures > BMI > lesion depth > lesion location > needle diameter. The nomogram demonstrated robust calibration and predictive accuracy, with C-index values of 0.877 (training set) and 0.897 (validation set). The areas under the ROC curve (AUC) were 0.875 (95 % CI: 0.825-0.926) and 0.897 (95 % CI: 0.829-0.965), respectively. Sensitivity and specificity were 0.855/0.813 (training set) and 0.765/0.823 (validation set).
Conclusion: Key determinants of postprocedural pneumothorax in GGN patients were identified through logistic regression and nomogram modeling. The validated predictive model exhibited excellent discriminative ability and clinical applicability, providing a scientific basis for individualized risk assessment and intervention strategies.
Keywords: CT-guided percutaneous biopsy; Ground-glass nodule; Logistic regression; Microwave ablation; Pneumothorax.
Copyright © 2025 HCFMUSP. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Yoshida R., Yoshizako T., Tanaka S., Ando S., Nakamura M., Kishimoto K., et al. CT-guided color marking of impalpable pulmonary nodules prior to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Clin Imaging. 2021;74:84–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

