Prevalence and associated outcomes of right ventricular dysfunction in peripartum cardiomyopathy: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
- PMID: 40819912
- PMCID: PMC12359473
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2025-003253
Prevalence and associated outcomes of right ventricular dysfunction in peripartum cardiomyopathy: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
Abstract
Introduction: Recent studies have highlighted the presence of right ventricular dysfunction (RVD) in a substantial proportion of peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), with evidence suggesting that RVD is associated with worse outcomes and a lower likelihood of left ventricular (LV) recovery. This study aims to comprehensively assess the pooled prevalence, associated outcomes and LV recovery of RVD in PPCM.
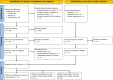
Methods: PubMed, Scopus and ScienceDirect were used to identify relevant literature prior to 19 January 2025. Statistical analysis was conducted using RStudio. All meta-analyses were performed using random effects, with subsequent subgroup analysis and univariate meta-regression conducted for prevalence meta-analysis.
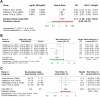
Results: The pooled prevalence of RVD in PPCM was 0.48 (95% CI: 0.36 to 0.59; I² 95.3%) across 14 studies (1385 patients). RVD was diagnosed using multimodality imaging (e.g., echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging), with diagnostic criteria defined in the original studies. Meta-regression showed a decreasing trend in RVD prevalence in more recent publications (p=0.03), with variability based on study design, location and diagnostic modality on subgroup analysis. Patients with RVD had a significantly higher risk of composite adverse outcomes (including death, LV assist device implantation, heart transplantation or the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; hazard ratio 2.71; 95% CI 1.08 to 6.84; p=0.04; three studies) and heart transplantation (risk ratio (RR) 4.71; 95% CI 1.82 to 12.20; p<0.01; two studies). Additionally, RVD was associated with a lower baseline LV ejection fraction (mean difference -10.94; 95% CI -14.80 to -7.08; p<0.01; six studies) and an increased risk of unrecovered LV function (RR 1.62; 95% CI 1.25 to 2.11; p<0.01; four studies).
Conclusion: RVD occurs in nearly half of patients with PPCM and is associated with a poor prognosis. It may represent a crucial marker for prognostic stratification, particularly for the risk of unrecovered LV function.
Prospero registration number: CRD42025626739.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathies; Heart Failure; Meta-Analysis; Pregnancy; Systematic Reviews as Topic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
