Optimization of PES-based Hollow fiber membranes incorporating MgO-modified activated carbon via response surface methodology for enhanced pure water permeability
- PMID: 40820019
- PMCID: PMC12358607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15140-3
Optimization of PES-based Hollow fiber membranes incorporating MgO-modified activated carbon via response surface methodology for enhanced pure water permeability
Abstract
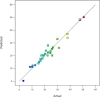
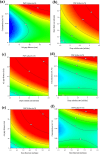
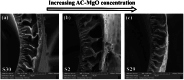
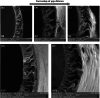
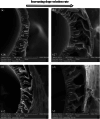
This research aims to optimize the fabrication of polyethersulfone (PES)-based composite hollow fiber membranes via phase inversion. For this purpose, MgO-modified activated carbon (AC) particles were synthesized and incorporated into the polymer matrix. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were utilized to examine the morphological and chemical properties of the AC-MgO particles. To optimize the fabrication process, the effects of four key parameters: AC-MgO particle concentration (0.09-0.36 wt%), bore fluid flow rate (3.5-9.5 ml/min), dope solution flow rate (1.5-3.5 ml/min), and air gap distance (2-42 cm), were analyzed using response surface methodology (RSM) with a central composite design. The performance of the membranes was assessed in terms of pure water permeability (PWP). The results of experimental tests conducted under the optimal conditions obtained using the RSM method for particle concentration and process parameters were in close agreement with the model predictions, confirming the model's accuracy. Moreover, it was found that particle concentration and air gap distance significantly influenced membrane performance. The AC-MgO particles significantly enhanced membrane properties by reducing the water contact angle, indicating improved hydrophilicity, and promoting the formation of a more porous membrane structure.
Keywords: AC-MgO particles; Hollow fiber membrane; Morphology; RSM; Spinning parameters.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Baker, R. W. Membrane Technology and Applications 3rd edn 303–324 (Wiley, 2012).
-
- Siagian, U. W. R. et al. High-performance ultrafiltration membrane: recent progress and its application for wastewater treatment. Curr. Pollut Rep.7, 448–462 (2021).
-
- Ding, X. et al. The enhancement of separation performance of Hollow fiber membrane modules: From the perspective of membranes and membrane modules structural optimization design. Chem. Eng. Sci.280, 2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

