Regulatory role of LncRNA FMR1-AS1 in the pathogenesis of alzheimer's disease based on bioinformatics and in vitro experimental validation
- PMID: 40820106
- PMCID: PMC12358618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15242-y
Regulatory role of LncRNA FMR1-AS1 in the pathogenesis of alzheimer's disease based on bioinformatics and in vitro experimental validation
Abstract
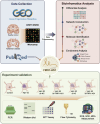
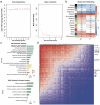
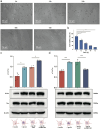
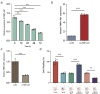
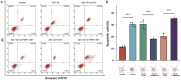
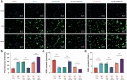
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a major cause of dementia, characterized by β-amyloid (Aβ) plaque accumulation and Tau protein hyperphosphorylation. Although long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, their roles in AD remain unclear. This study analyzed RNA sequencing data from the brain tissues of 17 AD patients and 19 healthy controls (GEO: GSE138260) to construct a gene co-expression network and identified eight lncRNAs strongly associated with AD. FMR1-AS1 was selected for functional validation. In an Aβ1-42-induced SH-SY5Y neuronal injury model, overexpression of FMR1-AS1 significantly increased cell viability ([Formula: see text]), inhibited apoptosis ([Formula: see text]), and reduced Tau hyperphosphorylation ([Formula: see text]). FMR1-AS1 also alleviated oxidative stress by lowering reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels ([Formula: see text]), enhanced superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity ([Formula: see text]), and decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) content ([Formula: see text]). Knockdown of FMR1-AS1 exacerbated neuronal damage. These results demonstrate that FMR1-AS1 exerts neuroprotective effects by regulating apoptosis, oxidative stress, and Tau pathology. The study highlights FMR1-AS1 as a potential therapeutic target for AD and may advance the understanding of lncRNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms in neurodegeneration.
Keywords: FMR1-AS1; Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ1–42; Bioinformatics; Neuronal cells; Oxidative stress; Tau phosphorylation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
The soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU alleviates Aβ-mediated neuroinflammatory responses in Drosophila melanogaster and cellular models of alzheimer's disease.J Inflamm (Lond). 2025 Jun 23;22(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12950-025-00449-7. J Inflamm (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40551105 Free PMC article.
-
Saikosaponin C ameliorates tau-related pathology by modulating oxidative stress and MAPK axis in Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120221. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120221. Epub 2025 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40588144
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
References
Grants and funding
- STKJ202209017/Guangdong Province Special Fund for Science and Technology Project
- STKJ2023012/Guangdong Science and Technology Plan Projects
- 2025A1515012810/Natural Science Foundation of Guang-dong Province
- 62002212/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024ZD0529106/National Science and Technology Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

