Positional and dimensional temporomandibular joint osseous changes in patients treated with the forsus fatigue resistant device: a non-randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 40820194
- PMCID: PMC12358331
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-025-06474-3
Positional and dimensional temporomandibular joint osseous changes in patients treated with the forsus fatigue resistant device: a non-randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the osseous positional and dimensional changes in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) of patients with skeletal Class II malocclusion treated with the Forsus Fatigue Resistant Device (FFRD).
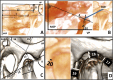
Materials and methods: This non-randomized clinical trial included 40 female subjects, aged 11 to 15, with skeletal Class II malocclusion. Participants were divided into a treatment and a control group. After alignment and leveling with fixed orthodontic appliances using 0.019 × 0.025-inch stainless-steel archwires, the FFRD was fitted. The overjet was corrected to achieve an edge-to-edge incisor relationship. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) images were taken before (T1) and after (T2) the fixed functional phase. The TMJs were assessed for positional and dimensional osseous changes in the mandibular condyles, glenoid fossae, and joint spaces. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were conducted using paired t-tests and independent t-tests, respectively.
Results: The initial measurements of age, cervical stage, anteroposterior and vertical skeletal alignment, and TMJ parameters were similar between the study and control groups. Three participants from the study group were lost to follow-up, resulting in 17 participants completing the trial. In the treatment group, condylar width decreased significantly by 0.52 ± 0.92 mm, in contrast to an increase of 0.17 ± 0.35 mm in the control group (P = 0.010). Moreover, the anterior wall inclination in the treatment group was reduced by 3.13 ± 10.77 degrees, compared to an increase of 2.95 ± 4.1 degrees in the control group (P = 0.003). All other measurements displayed no significant differences between the two groups.
Conclusion: In the short term, the FFRD redirected the growth of the articular eminence anteriorly, contrasting with the normal growth pattern of untreated individuals. However, no additional positional or dimensional changes in the TMJ were observed.
Clinical relevance: By aligning the jaw and correcting overjet, clinicians can potentially enhance occlusal relationships and contribute to better jaw function. However, it is important to investigate whether this process is associated with any changes in the bony structures of the TMJ. This study underscores the efficacy of the FFRD in reshaping the osseous components of the TMJ, which may lead to improved functional outcomes for patients with skeletal Class II malocclusion.
Keywords: CBCT; Class II malocclusion; Fixed functional appliances; Forsus fatigue resistant device; Growth modification; Temporomandibular joint.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Cairo University in Egypt (IRB: 5/15-07-1220). All patients treated at the orthodontic department of Cairo University are requested to sign a consent that allows the use of their treatment records for research purposes. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Orthodontic treatment for prominent lower front teeth (Class III malocclusion) in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 10;4(4):CD003451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003451.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38597341 Free PMC article.
-
Orthodontic treatment for prominent upper front teeth (Class II malocclusion) in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 13;(11):CD003452. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003452.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 13;3:CD003452. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003452.pub4. PMID: 24226169 Updated.
-
Orthodontic treatment for prominent upper front teeth in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD003452. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003452.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17636724
-
Orthodontic treatment for prominent upper front teeth (Class II malocclusion) in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 13;3(3):CD003452. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003452.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29534303 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in temporomandibular joint morphology in class II patients treated with fixed mandibular repositioning and evaluated through 3D imaging: a systematic review.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2015 Nov;18(4):185-201. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12099. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2015. PMID: 26260422
References
-
- Shalu S, Rai R, Sudhakar SS, Kannan G (2022) Comparison of skeletal effects of forsus fatigue resistant device and powerscope treatment–a cephalometric study. Ann Rom Soc Cell Biol 26:134–142
-
- Bavbek NC, Tuncer BB, Turkoz C, Ulusoy C, Tuncer C (2016) Changes in airway dimensions and hyoid bone position following class II correction with forsus fatigue resistant device. Clin Oral Investig 20:1747–1755 - PubMed
-
- Insabralde NM, de Almeida MR, de Almeida-Pedrin RR, Flores-Mir C, Henriques JFC (2021) Retrospective comparison of dental and skeletal effects in the treatment of class II malocclusion between herbst and Xbow appliances. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 160:544–551 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

