Rituximab plus chemotherapy for pediatric mature B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40821041
- PMCID: PMC12351614
- DOI: 10.62347/GOXN1938
Rituximab plus chemotherapy for pediatric mature B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of rituximab combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of mature B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) in children and adolescents.
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science was performed to identify relevant studies published up to October 2024. Eligible studies included those involving patients aged 0-15 years diagnosed with mature B-cell NHL. Data were extracted on event-free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS), complete remission rate (CRR), adverse events, immune reconstitution (IgG levels), and recurrence rates. Meta-analyses were conducted using RevMan 5.0.
Results: A total of 11 studies comprising 1,522 participants were included. The addition of rituximab to chemotherapy significantly improved EFS (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.40, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.36-0.45, P < 0.05) and OS (HR = 0.38, 95% CI: 0.34-0.42, P < 0.05). CRR was also significantly higher in the rituximab group (odds ratio [OR] = 2.72, 95% CI: 1.76-4.21, P < 0.05). However, a higher incidence of adverse effects was observed (OR = OR= 1.92, 95% CI: 1.25-2.94, P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in recurrence rate or IgG levels between groups.
Conclusion: The addition of rituximab to chemotherapy significantly improved EFS, OS, and CRR in children and adolescents with mature B-cell NHL. Despite an increased risk of toxicity, the survival and remission benefits support the use of rituximab in this population.
Keywords: Rituximab treatment; chemotherapy regime; children and adolescents; effectiveness and safety; mature B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





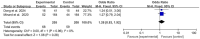
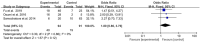

References
-
- Sapkota S, Shaikh H. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Hira Shaikh declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2025.
-
- Alexander S, Aupérin A, Bomken S, Csóka M, Kazanowska B, Chiang AK, Andres M, Uyttebroeck A, Burke GAA, Zsiros J, Pillon M, Bollard CM, Mussolin L, Verdu-Amoros J, Neven B, Barkauskas DA, Wheatley K, Patte C, Gross TG, Minard-Colin V Children’s Oncology Group; European Intergroup for Childhood Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Effect of rituximab on immune status in children with mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a prespecified secondary analysis of the Inter-B-NHL Ritux 2010 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023;10:e445–e457. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burke GAA, Vinti L, Kabickova E, Beishuizen A, Tacyildiz N, Uyttebroeck A, Kang HJ, Luisi F, Minard-Colin V, Burkhardt B, Tamegnon M, Sun S, Curtis M, Deshpande S, Nottage K, Howes A, Srinivasan S, Bhojwani D, Norris R, Cairo M. Ibrutinib plus RICE or RVICI for relapsed/refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and young adults: SPARKLE trial. Blood Adv. 2023;7:602–610. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bethke M, Varga G, Weinhage T, Sabharwal H, Mellgren K, Randau G, Rolfing M, Wittkowski H, Foell D, Michgehl U, Burkhardt B. Patient parameters and response after administration of rituximab in pediatric mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022;69:e29514. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
