Acupuncture combined with pelvic floor muscle training for treating postpartum stress urinary incontinence
- PMID: 40821061
- PMCID: PMC12351554
- DOI: 10.62347/ICCK8666
Acupuncture combined with pelvic floor muscle training for treating postpartum stress urinary incontinence
Abstract
Objective: To explore the clinical application of acupuncture combined with pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) in treating postpartum stress urinary incontinence (PSUI) based on patient data.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 97 PSUI patients treated at the Second People's Hospital of Nantong from July 2021 to June 2023. Patients voluntarily chose between the two treatment groups: PFMT alone or the combination of acupuncture and PFMT. Multiple indicators, including pad test positive rate, urinary scores, leakage volume, incontinence degree, treatment effectiveness, pelvic floor muscle strength, and sexual quality of life, were compared between the two groups.
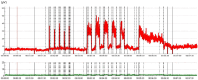
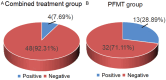
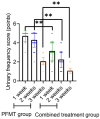
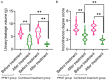
Results: The pad test positive rate was significantly lower in the combined treatment group (7.69%) than in the PFMT group (28.89%) (P = 0.013). The combined treatment group had lower urinary scores (t = 9.288-16.020, all P < 0.001) and higher overall efficacy (92.31% vs. 68.89%, P < 0.05). Both groups demonstrated improved pelvic floor muscle strength, with the combined intervention group showing greater enhancement compared to PFMT alone (P < 0.05). Urinary leakage volume and incontinence degree scores decreased more in the combined treatment group (P < 0.001) than in the PFMT group (P < 0.001 between groups). The combined treatment group had better sexual quality of life and greater reductions in SAS and SDS scores (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Acupuncture combined with PFMT demonstrated significantly superior outcomes to PFMT alone for PSUI treatment, with significant improvements in incontinence symptoms, psychological status, muscle strength, and quality of sexual life. Findings support the clinical adoption of this combined strategy for PSUI.
Keywords: Acupuncture; efficacy; pelvic floor muscle training; postpartum; stress urinary incontinence.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Retrospective Study of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Combined with Biofeedback Stimulation versus Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Alone in the Treatment of Postpartum Stress Urinary Incontinence.Arch Esp Urol. 2025 Jul;78(6):684-692. doi: 10.56434/j.arch.esp.urol.20257806.92. Arch Esp Urol. 2025. PMID: 40776867
-
Pelvic floor muscle training with feedback or biofeedback for urinary incontinence in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 11;3(3):CD009252. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009252.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40066950
-
Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD007471. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007471.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 6;5:CD007471. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007471.pub4. PMID: 29271473 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparisons of approaches to pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 20;12(12):CD009508. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009508.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39704322
-
Conservative interventions for treating urinary incontinence in women: an Overview of Cochrane systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 2;9(9):CD012337. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012337.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36053030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He Y, Liu L, Dong W, Luo H, Yang Y, Ning G, Xiao Y. Evaluation of the curative effect of the combination of warm acupuncture and pelvic floor muscle exercise in female stress urinary incontinence by real-time three-dimensional pelvic floor ultrasound. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound in Medicine. 2018;20:823–825.
-
- Brennen R, Frawley HC, Martin J, Haines TP. Group-based pelvic floor muscle training for all women during pregnancy is more cost-effective than postnatal training for women with urinary incontinence: cost-effectiveness analysis of a systematic review. J Physiother. 2021;67:105–114. - PubMed
-
- Nambiar AK, Arlandis S, Bø K, Cobussen-Boekhorst H, Costantini E, de Heide M, Farag F, Groen J, Karavitakis M, Lapitan MC, Manso M, Arteaga SM, Riogh ANA, O’Connor E, Omar MI, Peyronnet B, Phé V, Sakalis VI, Sihra N, Tzelves L, van Poelgeest-Pomfret ML, van den Bos TWL, van der Vaart H, Harding CK. European Association of Urology Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Female Non-neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Part 1: diagnostics, overactive bladder, stress urinary incontinence, and mixed urinary incontinence. Eur Urol. 2022;82:49–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
