Intra-articular sodium hyaluronate, compound betamethasone, and ropivacaine combined with arthroscopic debridement in patients with knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 40821079
- PMCID: PMC12351615
- DOI: 10.62347/BNMD7591
Intra-articular sodium hyaluronate, compound betamethasone, and ropivacaine combined with arthroscopic debridement in patients with knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of sodium hyaluronate (SH), compound betamethasone (BT), and ropivacaine (Rop) in combination with arthroscopic debridement (AD) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
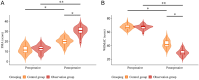
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 107 KOA patients treated at Shantou Central Hospital l, including 52 patients in the control group who received AD alone and 55 patients in the observation group who additionally received intra-articular SH, compound BT, and Rop. Treatment efficacy, pain levels, knee joint function, lower limb motor function, serum inflammatory markers, quality of life, and sleep quality were assessed and compared between the two groups. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify factors influencing treatment outcomes.
Results: The observation group showed significantly better outcomes than the control group in terms of overall treatment efficacy, pain relief, improvement in joint and lower limb function, reduction in inflammatory markers, and enhancement of both sleep quality and overall quality of life. Prolonged disease duration was identified as an independent risk factor for poor treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: The combination of SH, compound BT, and Rop with AD offers significant clinical advantages in the management of KOA, supporting its broader adoption in clinical practice.
Keywords: Knee osteoarthritis; arthroscopic debridement; compound betamethasone; ropivacaine; sodium hyaluronate.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Kan HS, Chan PK, Chiu KY, Yan CH, Yeung SS, Ng YL, Shiu KW, Ho T. Non-surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Hussain SM, Neilly DW, Baliga S, Patil S, Meek R. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of management options. Scott Med J. 2016;61:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Giwnewer U, Rubin G, Orbach H, Rozen N. Treatment for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Harefuah. 2016;155:403–406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
