Predictive value of NLR, PLR and MPVLR for recent major cardiovascular adverse events in elderly patients with heart failure
- PMID: 40821098
- PMCID: PMC12351568
- DOI: 10.62347/XQNT2355
Predictive value of NLR, PLR and MPVLR for recent major cardiovascular adverse events in elderly patients with heart failure
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the application value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and mean platelet volume to lymphocyte ratio (MPVLR) levels in identifying recent major cardiovascular adverse events (MACE) in elderly patients with heart failure (HF).
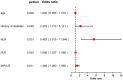
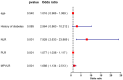
Method: A total of 103 elderly HF patients admitted to Suzhou Hospital affiliated to Anhui Medical University from January 2022 to February 2025 were selected as the model group, and 74 patients from the same period served as the external validation group. All patients were followed up for 3 months after treatment. Patients were categorized into a MACE group and a non-MACE group based on the occurrence of MACE. Clinical data and levels of NLR, PLR, and MPVLR, were compared between the two groups. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify the independent risk factors for recent MACE. A forest plot was drawn using Graphpad Prism 8.0 software. Predictive models were evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and calibration curves.
Results: Patients in the MACE group were older and had a higher prevalence of diabetes compared to the non-MACE group. Levels of NLR, PLR, and MPVLR were significantly elevated in the MACE group. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified NLR (OR = 7.928, 95 CI 2.633-23.869), PLR (OR = 1.077, 95 CI 1.038-1.117), MPVLR (OR = 1.688, 95 CI 1.134-2.513) as risk factors for recent MACE in elderly HF patients (all P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that the combined use of NLR, PLR, and MPVLR had superior predictive performance compared to individual indicators (P < 0.05). The predictive model demonstrated superior discriminative ability compared to individual indicators (AUC = 0.919), which was further validated in the external validation group (AUC = 0.810), indicating consistent predictive accuracy.
Conclusion: Elevated levels of NLR, PLR, and MPVLR can serve as independent risk factors for assessing the risk of recent MACE in elderly HF patients. The combined predictive model demonstrates high accuracy and may assist in early risk stratification and personalized preventive strategies to reduce the risk of MACE.
Keywords: Elderly heart failure; major cardiovascular adverse events; mean platelet volume to lymphocyte ratio; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; platelet to lymphocyte ratio.
AJTR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The comparative and added prognostic value of biomarkers to the Revised Cardiac Risk Index for preoperative prediction of major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality in patients who undergo noncardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 21;12(12):CD013139. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013139.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34931303 Free PMC article.
-
Association of platelet-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio with coronary heart disease prevalence in asthma patients: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 1999-2018.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jun 30;17(6):3831-3839. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1761. Epub 2025 Jun 13. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688335 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between lymphocyte-related parameters and the prognosis of patients with lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1613483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613483. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40698075 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR), and Eosinophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (ELR) as Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD).Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Feb 23;19:501-518. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S447519. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 38414718 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Markers and Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Risk: A Meta-Analysis of NLR and PLR in ACS Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Aug 5. doi: 10.1002/ccd.70056. Online ahead of print. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2025. PMID: 40762252 Review.
References
-
- Díez J, Butler J. Growing heart failure burden of hypertensive heart disease: a call to action. Hypertension. 2023;80:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Chai K, Du M, Wang S, Cai JP, Li Y, Zeng P, Zhu W, Zhan S, Yang J. Prevalence and incidence of heart failure among urban patients in China: a national population-based analysis. Circ Heart Fail. 2021;14:e008406. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrino R, Paganelli R, Di Iorio A, Bandinelli S, Moretti A, Iolascon G, Sparvieri E, Tarantino D, Ferrucci L. Temporal trends, sex differences, and age-related disease influence in neutrophil, lymphocyte count and neutrophil to lymphocyte-ratio: results from InCHIANTI follow-up study. Immun Ageing. 2023;20:46. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
