Pediatric Pharmacy Association 2025 KIDs List of Key Potentially Inappropriate Drugs in Pediatrics
- PMID: 40821415
- PMCID: PMC12351480
- DOI: 10.5863/JPPT-25-00061
Pediatric Pharmacy Association 2025 KIDs List of Key Potentially Inappropriate Drugs in Pediatrics
Abstract
Objective: The objective was to update the KIDs List, a list of drugs and excipients that are potentially inappropriate for use in pediatric patients, accounting for emerging pharmacologic agents and published evidence.
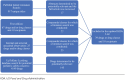
Methods: A panel of 12 pediatric pharmacists from the Pediatric Pharmacy Association (PPA) evaluated primary, secondary, and tertiary literature; FDA Pediatric Safety Communications; the UpToDate Lexidrug database; and product information for drugs that may be considered potentially inappropriate for use in pediatric patients. A PubMed search identified new publications from October 1, 2017, to November 1, 2023. All agents included in the previous publication and those anecdotally identified as candidates for the list by the authors or PPA members were evaluated. Evidence was reviewed by all authors. The draft list underwent a 30-day public comment period prior to being finalized.
Results: A PubMed search yielded 917 unique titles of which 17 were deemed relevant for full review. Sixty-seven drugs and/or drug classes and 10 excipients from the original publication were also reviewed. Author and PPA member recommendations highlighted an additional 25 drugs or drug classes. The UpToDate Lexidrug database extraction yielded 1470 drugs, which were filtered to 145 agents for author review. After critical analysis and reorganization, the second edition of the KIDs List contains 39 drugs and/or drug classes and 10 excipients.
Conclusions: This article updates the initial list of drugs and excipients that are potentially inappropriate for prescribing in all or a select subgroup of pediatric patients. The second edition should stimulate novel research to inform future updates.
Keywords: adverse drug event; adverse drug reaction; excipients; medications; pediatrics; potentially inappropriate medication list.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: membership@pediatricpharmacy.org.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA. 1998;279(15):1200–1205. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources