Bioinspired Lignin-Aluminosilicate Composite for CO2 Storage
- PMID: 40821565
- PMCID: PMC12355257
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c04745
Bioinspired Lignin-Aluminosilicate Composite for CO2 Storage
Abstract
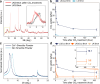
In the effort to decarbonize hard-to-abate industries, the issue of CO2 emissions from the cement production process must be addressed, primarily due to the calcination reaction and high-temperature requirements. To achieve a sustainable process to produce carbon-neutral construction materials, utilizing nature-abundant resources without relying on calcium oxide chemistry or sintering could be a promising approach. Here, a new method is presented to prepare construction material by strengthening highly abundant kaolinite clay with Kraft lignin at 100 °C. Due to the electrostatic interactions between Kraft lignin and kaolinite particles, the resulting lignin-aluminosilicate composite displayed compressive strengths of up to 20 MPa. Additionally, the simultaneous use of kaolinite and smectite enabled the fabrication of a strong composite, which could store up to 10 g of CO2 per 1 kg under high-pressure CO2 treatment at room temperature. Furthermore, the scalability of the proposed method to real-sized bricks and artworks was demonstrated, thereby opening new pathways toward a carbon-negative construction industry.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures




References
-
- Czigler, T. ; Reiter, S. ; Schulze, P. ; Somers, K. . Laying the Foundation for Zero-Carbon Cement; McKinsey & Company; 2020, 9.
-
- Industry - Energy System - IEA , 2024, https://www.iea.org/energy-system/industry (accessed 2024–09–20).
-
- Sprung, S. Cement. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2000.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
