Enhanced cancer cell sorting using lab-on-a-disk pattern design with magnetic and centrifugal forces
- PMID: 40821671
- PMCID: PMC12354510
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1611313
Enhanced cancer cell sorting using lab-on-a-disk pattern design with magnetic and centrifugal forces
Abstract
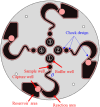
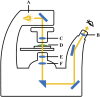
Using microfluidic flow for biological detection is a non-invasive method that can replace traditional invasive testing methods to achieve fast and accurate results. The design of the detection device and lab-on-a-disk (LoaD) can impact performance in accurately identifying biological features. Therefore, we created a novel device to extract cancer cells from a heterogeneous cell population by centrifugal-force-driven microfluidic flow and magnetic labeling. Two-stage centrifugal force and a specially designed LoaD were used to drive microfluidic flow and control its movement to designated areas. The purpose was to allow the CD44 antibody-magnetic bead complex (CD44 beads), which specifically binds to the abundantly present CD44 receptors on identifiable cancer cells, to flow into the reservoir well, while the biological mixture containing the cancer cells is retained in the capture well. Fluorescence imaging as well as flow cytometric analysis revealed the successful retention of the microbead-bound cancer cells in the magnetic area, while the remaining biological mixture was retained in the reservoir area. The entire separation process took less than 2 h.
Keywords: cell sorting; lab-on-a-disk; microfluidic flow; non-invasive method; rapid detection.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Chao, Chen and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Novel application of metabolic imaging of early embryos using a light-sheet on-a-chip device: a proof-of-concept study.Hum Reprod. 2025 Jan 1;40(1):41-55. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae249. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 39521726 Free PMC article.
-
Automated devices for identifying peripheral arterial disease in people with leg ulceration: an evidence synthesis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Aug;28(37):1-158. doi: 10.3310/TWCG3912. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39186036 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya S., Chhabra J., Mukherji S., Paul D. (2023). A low-cost and portable centrifugal microfluidic platform for continuous processing of large sample volumes. AIP Adv. 13, 1. 10.1063/5.0128239 - DOI
-
- Bertsche D., Knipper P., Kapfer K., Wetzel T. (2019). Experimental investigation on heat transfer in laminar, transitional and turbulent circular pipe flow with respect to flow regime boundaries. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 145, 118746. 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118746 - DOI
-
- Branderhorst G. J. H. J. (2024). Automatic characterization of a DC motor. University of Twente. Available online at: https://purl.utwente.nl/essays/100959.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

