Prospective validation of the Barcelona scale for the assessment of mucosal cleanliness during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
- PMID: 40821738
- PMCID: PMC12357016
- DOI: 10.1177/17562848251363873
Prospective validation of the Barcelona scale for the assessment of mucosal cleanliness during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Abstract
Background: Some validated scales for assessing upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cleanliness have been developed, though none have been widely implemented.
Objectives: To evaluate the association between the presence of clinically significant lesions (CSLs) in the UGI tract and mucosal cleanliness using the Barcelona Scale. The secondary objective includes assessing the safety of water lavage during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
Design: Multicenter prospective study conducted in 14 hospitals in Spain.
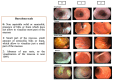
Methods: From January 2022 to December 2023, patients undergoing EGD were included. After cleansing, the esophagus, fundus, corpus, antrum, and duodenum were scored from 0 (unassessable due to content) to 2 (fully visualized mucosa), with a maximum score of 10.
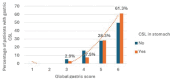
Results: A total of 641 patients were included, and 3205 segments were assessed: 2594 scored "2," 604 "1," and 7 "0." In 272 patients, 327 CSLs were identified: 93 (14.5%) in the esophagus, 223 (34.8%) in the stomach, and 11 (1.7%) in the duodenum. Only five cases of neoplasia were found, all in segments scored "2" (global score ⩾ 9). The CSL detection rates were 0%, 5.3%, and 11.4% for scores 0, 1, and 2, respectively (p < 0.001), with a significantly higher rate for score "2" compared to "1" (OR 2.29, 95% CI 1.57-3.34). Besides the degree of cleanliness, several factors were independently associated with CSL detection, including the use of a high-definition endoscope (OR 1.87, 95% CI 1.14-3.23), male sex (OR 1.54, 95% CI 1.1-2.17), and age ⩾58 years (OR 1.54, 95% CI 1.09-2.17).
Conclusion: The Barcelona scale may be a valid instrument for assessing the quality of cleanliness during EGD in real clinical practice, as it improves the detection of CSL in the UGI.
Keywords: cleanliness; esophagogastroduodenoscopy; quality; upper gastrointestinal tract; visualization.
Plain language summary
The Barcelona scale is a valid and safe instrument for assessing the quality of cleanliness during EGD in real clinical practice This study prospectively assessed the validity of the Barcelona Cleanliness scale as a tool for evaluating cleanliness during real-time EGD and demonstrated its significant association with the detection of CSL. This clear and simple scale is a 3-point scoring system (0 to 2) that assesses the entire upper GI tract (esophagus, stomach and duodenum) and divides the stomach into three segments: fundus, body and antrum. The Barcelona scale has demonstrated to be a valid and reproducible scale with minimal training among endoscopists with different levels of expertise. We believe these findings might help endoscopists to assess the mucosal cleanliness quality during EGD, using the Barcelona scale.
© The Author(s), 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Delgado Guillena PG, Morales Alvarado VJ, Jimeno Ramiro M, et al. Gastric cancer missed at esophagogastroduodenoscopy in a well-defined Spanish population. Dig Liver Dis 2019; 51: 1123–1129. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Esparrach G, Marín-Gabriel JC, Díez Redondo P, et al. Documento de posicionamiento de la AEG, la SEED y la SEAP sobre calidad de la endoscopia digestiva alta para la detección y vigilancia de las lesiones precursoras de cáncer gástrico. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 44: 448–464. - PubMed
-
- Bisschops R, Areia M, Coron E, et al. Performance measures for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) quality improvement initiative. Endoscopy 2016; 48: 843–864. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources