Advances in the Role of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Diabetic Foot Wound Healing
- PMID: 40821749
- PMCID: PMC12350548
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S521095
Advances in the Role of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Diabetic Foot Wound Healing
Abstract
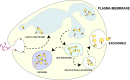
Chronic hyperglycemia over a long period can lead to diabetes-related complications, of which diabetic foot ulcers continue to have a huge economic and social impact worldwide. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) have demonstrated positive efficacy in the preclinical research and clinical trial phases of diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) treatment. In this review, we provide a brief overview of the properties of MSC-derived exosomes and their biological functions, summarize the therapeutic efficacy of Exos in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and its mechanism of action, and discuss innovative technologies including hydrogel scaffolds and 3D bioprinting to enhance the effectiveness of MSC - Exos in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. This paper also explores the application of innovative technologies such as hydrogel scaffolds and 3D bioprinting in enhancing the efficacy of MSC-Exos in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and highlights the key challenges faced in translating these advanced technologies from the laboratory to the clinic.
Keywords: chronic wounds; diabetic foot ulcers; stem cell-derived exosomes; tissue engineering; translational research.
© 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Similar articles
-
The Promising Hydrogel Candidates for Preclinically Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023 Jan;12(1):28-37. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0162. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2023. PMID: 35229628
-
Advancements in diabetic foot ulcer therapy: The role of exosomes and decellularised extracellular matrix scaffolds.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2025 Aug;226:112364. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2025.112364. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 40651532 Review.
-
Topical antimicrobial agents for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 14;6(6):CD011038. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011038.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28613416 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for treating foot ulcers, and preventing their recurrence, in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 8;2(2):CD012835. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012835.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 35653236 Free PMC article.
-
Growth factors for treating diabetic foot ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 28;2015(10):CD008548. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008548.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26509249 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources