Identification of circRNA expression signatures correlated with disease severity in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 40821807
- PMCID: PMC12350355
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1608509
Identification of circRNA expression signatures correlated with disease severity in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex systemic autoimmune disease with no current cure. Developing diagnostic biomarkers is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs that are more stable, abundant, and structurally distinct compared to linear RNAs. While circRNAs have shown promise as biomarkers in various diseases, their potential in pediatric SLE remains unclear.
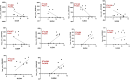
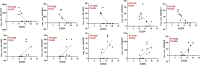
Methods: We performed RNA sequencing on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from pediatric SLE patients categorized into mild, moderate, and severe groups. CircRNA expression profiles were analyzed for differential expression. The potential of circRNAs as biomarkers for SLE severity was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Additionally, Spearman correlation analysis was used to assess the relationship between circRNA expression levels and the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) score.
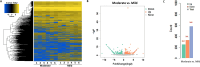
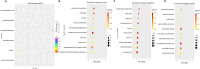
Results: Our analysis revealed significant differential expression of circRNAs across different SLE severity groups. The circRNA expression patterns were closely associated with various biological processes, including signaling pathways, metabolism, and transcriptional regulation. Furthermore, ROC analysis demonstrated the potential of circRNAs to predict SLE severity. Spearman correlation analysis showed a significant correlation between dysregulated circRNA expression and SLEDAI scores.
Conclusion: Our findings strongly suggest that circRNAs could play a pivotal role in predicting pediatric SLE severity, offering a promising avenue for early diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. This research lays the groundwork for future studies exploring circRNAs in pediatric SLE pathogenesis and prognosis, with the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; biomarker; circRNA; disease activity; pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Chen, Tang, Cheng, Zeng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

