Health benefits of viewing nature through windows: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 40821892
- PMCID: PMC12352305
- DOI: 10.1093/biosci/biaf089
Health benefits of viewing nature through windows: A meta-analysis
Abstract
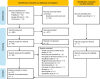
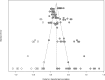
Experiencing nature offers numerous health and well-being benefits, particularly for urban residents. Although the benefits of visiting natural environments are well documented, less is known about the health effects of experiencing nature without going outdoors-in particular, viewing it through building windows. This meta-analysis synthesizes findings from 28 studies encompassing 104 results to examine the relationship between window views of nature and human health. Improvements were reported across various physiological, psychological, and physical health measures, with most studies focused on psychological outcomes. The meta-analytic results indicate consistently positive effects, with particularly strong benefits in studies using physiological health measures and focusing on nature in urban settings. Although some publication bias was detected, correcting for it did not change the overall conclusions. These findings highlight the potential of integrating nature views into built environments as a practical strategy for enhancing public health, particularly in urban areas.
Keywords: ecosystem services; human–nature interactions; nature dose; personalized ecology; urbanization.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Institute of Biological Sciences.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews M, Gatersleben B. 2010. Variations in perceptions of danger, fear, and preference in a simulated natural environment. Journal of Environmental Psychology 30: 473–481.
-
- Belussi L, et al. 2019. A review of performance of zero energy buildings and energy efficiency solutions. Journal of Building Engineering 25: 100772.
-
- Bixler RD, Floyd MF. 1997. Nature is scary, disgusting, and uncomfortable. Environment and Behavior 29: 443–467.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

