Tabernaemontana stapfiana Britten (Apocynaceae) Stem Bark Prevents Alcl3-Induced Cognitive Disability: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 40821960
- PMCID: PMC12352983
- DOI: 10.1155/omcl/5106228
Tabernaemontana stapfiana Britten (Apocynaceae) Stem Bark Prevents Alcl3-Induced Cognitive Disability: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Wistar Rats
Abstract
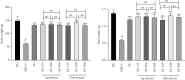
The present study aimed to evaluate the protective effects of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Tabernaemontana stapfiana (T. stapfiana) on cognitive disability induced by aluminum chloride (AlCl3) in Wistar rats. Forty-five Wistar rats were distributed in different groups of five animals each. Test groups were daily given AlCl3 (100 mg/kg) following by the doses of the extracts for 21 days. At the end of treatment period, rats were sacrificed and the brain homogenate and serum were prepared and used to evaluate oxidative stress in brain and serum cytokines using colorimetric tests and ELISA, respectively. The findings of this study showed that reduced brain, body weight, and antioxidant enzymes (reduced glutathione [GSH], catalase [CAT], and superoxide dismutase [SOD]), while it increases oxidant biomarkers (malondiadehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) and inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6). Therefore, the administration of aqueous or ethanol extracts of T. stapfiana stem bark significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the IL-10, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels in AlCl3-treated rats compared to non treated rats. Moreover, the extracts significantly (p < 0.001) changed the oxidant-antioxidant balance by reducing the MDA and NO levels, while increasing SOD and GSH concentrations caused and NO in AlCl3-treated rats as compared to nontreated rats. Conclusively, aqueous or ethanol extracts of T. stapfiana stem bark prevented the oxidative stress and inflammation in brain, which made the brain to be not change after administration of the causative agent of cognitive impairment (CI), AlCl3.
Keywords: Tabernaemontana stapfiana; cognitive impairment; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Mumbi Laurantine Ngenteh et al. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Effects of Moringa oleifera Against Abamectin-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Brain and Erythrocytes of Rats.Chem Biodivers. 2025 May;22(5):e202402709. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202402709. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39724495
-
The stem bark decoction of Myrianthus arboreus P. Beauv. (Cecropiaceae) shows anti-uterine leiomyoma effects in Wistar rat.Reprod Fertil. 2025 Jul 26;6(3):e250037. doi: 10.1530/RAF-25-0037. Print 2025 Jul 1. Reprod Fertil. 2025. PMID: 40626852 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferide and Norbergenin avert aluminium chloride-induced amyloid β accumulation and neurocognitive shutdown via oxidative and apoptotic mechanisms.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025 Jan-Dec;39:3946320251343687. doi: 10.1177/03946320251343687. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40590427 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of curcumin and selenium nanoparticles against aluminium chloride-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats.J Mol Histol. 2025 Jul 31;56(4):241. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10520-5. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40742469
-
Purslane Ameliorates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 15;25(22):12276. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212276. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zaher M. A. F., Bendary M. A., Aly A. S. Effect of Thymoquinone Against Aluminum Chloride-Induced Alzheimer-Like Model in Rats: A Neurophysiological and Behavioral Study. The Medical Journal of Cairo University . 2020;88(1):355–365.
-
- Ali N. A., Jaccob A. A., Al-Moziel M. S. G. Protective Effects of Co - Q10, Ginkgo biloba, and l - Carnitine on Brain, Kidney, Liver, and Endocrine System Against Sub - Acute Heavy Metals Toxicity in Male Rats. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences . 2020;12:331–341.
-
- Kaddour T., Omar K., Oussama A., Nouria H., Iméne B., Abdelkader A. Aluminium-Induced Acute Neurotoxicity in Rats: Treatment With Aqueous Extract of Arthrophytum (Hammada scoparia) Journal of Acute Disease . 2016;5(6):470–482.
-
- Shashani L. Aluminum Induced Neurotoxicity: A Review. Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences . 2020;9:63–71.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

