Evaluation of synthetic mRNA with selected UTR sequences and alternative poly(A) tail, in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 40822034
- PMCID: PMC12355064
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102648
Evaluation of synthetic mRNA with selected UTR sequences and alternative poly(A) tail, in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
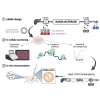
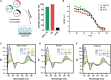
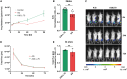
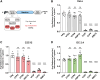
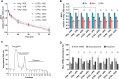
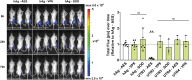
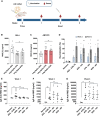
Messenger RNA (mRNA) has emerged as an attractive new technology of drugs. The efficacy of mRNA technology depends on both the efficiency of mRNA delivery and translation. Untranslated regions (UTRs) and the poly(A) tail play a crucial role in regulating mRNA intracellular kinetics. Intending to improve the therapeutic potential of synthetic mRNA, we evaluated various UTRs and tail designs, using Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine sequences as a reference. First, we screened six 5' UTRs (cap-dependent/-independent), evaluated nine 5' UTR-3' UTR combinations, and a novel heterologous A/G tail in cell models, and in vivo using luciferase as a reporter gene. Then, to decipher the translation mechanism of selected UTRs, we correlated mRNA expression with ribosome load, mRNA half-life, mRNA immunogenicity, and UTR structures. Our results showed that the heterologous tail we introduced is as potent as the Pfizer-BioNTech tail and confirmed the high potency of the human α-globin 5' UTR. They also revealed the potential of the VP6 and SOD 3' UTRs. We validated our results using mRNA encoding the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein formulated as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for mouse immunization. Overall, the selected 3' UTRs and heterologous A/G tail have great potential as new elements for therapeutic mRNA design.
Keywords: 3′ UTR; 5′UTR; MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; mRNA; mRNA stability; poly(A) tail; translation efficiency; vaccine.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.M., A.N., and F.P. are inventors of the patent WO2024231621 hold by CNRS related to the data in this work. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles Formulated with a Novel Cholesterol-Tailed Ionizable Lipid Markedly Increase mRNA Delivery Both in vitro and in vivo.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 28;20:9389-9405. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S527822. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40755461 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding post-transcriptional gene expression controls in trypanosomatids using machine learning.Wellcome Open Res. 2025 Jul 9;10:173. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.23817.2. eCollection 2025. Wellcome Open Res. 2025. PMID: 40735494 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing immunization: a comprehensive review of mRNA vaccine technology and applications.Virol J. 2025 Mar 12;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02645-6. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40075519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

