Transarterial Chemoembolization Following Curative Resection May Not Improve Survival for Hepatitis B Virus Associated Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Propensity Score Weighting Analysis
- PMID: 40822084
- PMCID: PMC12357570
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S518418
Transarterial Chemoembolization Following Curative Resection May Not Improve Survival for Hepatitis B Virus Associated Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Propensity Score Weighting Analysis
Abstract
Background: For hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) shows an advantageous response and prognosis in recurrent patients after resection. In consideration of similar pathogenesis and clinicopathological characteristics, studies should be conducted to ascertain whether hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) can be successfully treated by the methods used to treat HCC. The role of adjuvant TACE following liver resection for HBV-associated ICC remains controversial. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of adjuvant TACE on recurrence and survival after liver resection, both before and after propensity score weighting (PSW) analysis.
Materials and methods: A total of 356 patients were categorized into two groups: i) 77 patients who received adjuvant TACE, and ii) 279 patients who underwent R0 resection alone. Staging was conducted according to the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) staging system. Univariate and multivariate analyses were utilized to assess independent prognostic factors. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were compared using the Kaplan-Meier method.
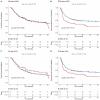
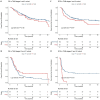
Results: Among the 356 enrolled patients, 77 received adjuvant TACE. The median follow-up period was 45.3 months. Adjuvant TACE did not significantly affect OS (P=0.629) before or after PSW. Subgroup analyses indicated that TACE was not associated with OS across different TNM stages. After propensity score weighting, Cox regression model indicated significantly increased recurrence risk with TACE (HR=1.53, 95% CI: 1.02-2.28; P=0.0071). Stage-specific risks were visually summarized in Supplementary Figure 1. Additionally, TACE did not significantly impact RFS in TNM stage I (P=0.1720) and stage II (P=0.7905) subgroups. Conversely, TACE was positively associated with increased recurrence risk in TNM stage III (P=0.0014) and stage IV (P=0.0051) patients.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that adjuvant TACE following radical surgery does not prolong OS for patients with HBV-associated ICC. Furthermore, adjuvant TACE was associated with increased recurrence risk in TNM Stage III and IV subgroups, though this observation requires further validation due to sample size limitations in advanced stages.
Keywords: HBV; ICC; PSW; TACE; hepatitis B virus; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; propensity score weighting; transarterial chemoembolization.
© 2025 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib for patients with HCC with MVI after resection: a multicenter retrospective study.Oncologist. 2025 Jun 4;30(6):oyaf139. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyaf139. Oncologist. 2025. PMID: 40504548 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization on the prognosis of early-stage intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a single center study.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):3673-3683. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1337. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33691434
-
Should patients with stage IB non-small cell lung cancer receive adjuvant chemotherapy? A comparison of survival between the 8th and 7th editions of the AJCC TNM staging system for stage IB patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;145(2):463-469. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2801-7. Epub 2018 Nov 24. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30474757 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different adjuvant therapy regimen efficacies in patients with high risk of recurrence after radical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10505-10518. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04874-0. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37284841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in rectal cancer operated for cure.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Mar 14;2012(3):CD004078. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004078.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22419291 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

