Light-Triggered Graphene/Black Phosphorus Heterostructure FET Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers at the Zeptomole Level
- PMID: 40822124
- PMCID: PMC12352878
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0772
Light-Triggered Graphene/Black Phosphorus Heterostructure FET Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers at the Zeptomole Level
Abstract
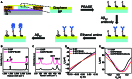
Due to the low concentration of amyloid-beta (Aβ) in plasma and the high content of interfering factors, the conventional detection method for the quantification of Aβ still faces the problem of insufficient limit of detection (LOD). In this work, we propose a new light-triggered graphene-black phosphorus heterostructure (G-BP) field-effect transistor (FET) biosensing platform that achieves a marked reduction in the LOD. The LOD for Alzheimer's disease (AD) biomarker Aβ42 detection using the G-BP FET is as low as 235.1 zM (2.351 × 10-19 M), which is the lowest value reported to date and is approximately 2 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than other reported biosensing platforms. The G-BP FET platform provides precise, real-time guidance for non-invasive early diagnosis, disease monitoring, and personalized treatment plans for AD. Moreover, this method has good scalability and potential applications in other areas, including early detection of cancer and other major chronic diseases.
Copyright © 2025 Huide Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Khachaturian ZS. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Neurol. 1985;42(11):1097–1105. - PubMed
-
- Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Sumi S, Crain BJ, Brownlee L, Vogel F, Hughes J, Belle G, Berg L. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s disease (Cerad). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1991;41(4):479–479. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

