Plate-Controlled Correction of Sagittal Plane Knee Deformities: The Entire-Segment Rotation Technique for Correcting Varus and Posterior Tibial Slope
- PMID: 40822204
- PMCID: PMC12350712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2025.103588
Plate-Controlled Correction of Sagittal Plane Knee Deformities: The Entire-Segment Rotation Technique for Correcting Varus and Posterior Tibial Slope
Abstract
Sagittal-plane deformity around the knee is usually overlooked. Correction of the sagittal plane may be performed alone or simultaneously with coronal plane correction. This proposed technique ensures an effective rotational control of the proximal tibial fragment along with precise intraoperative correction of the posterior tibial slope in degrees instead of millimeters, exactly as it was preplanned in degrees.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors (A.A., M.A., M.A.A.T., M.E.A., H.M.G.) declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
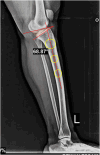
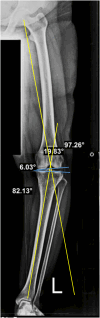

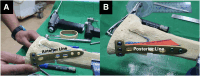

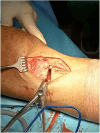
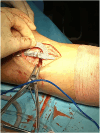




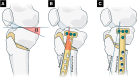
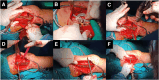
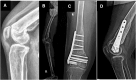
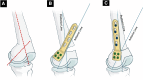
References
-
- Rodner C.M., Adams D.J., Diaz-Doran V., et al. Medial opening wedge tibial osteotomy and the sagittal plane: The effect of increasing tibial slope on tibiofemoral contact pressure. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34:1431–1441. - PubMed
-
- Song G.Y., Ni Q.K., Zheng T., Zhang Z.J., Feng H., Zhang H. Slope-reducing tibial osteotomy combined with primary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction produces improved knee stability in patients with steep posterior tibial slope, excessive anterior tibial subluxation in extension, and chronic meniscal posterior horn tears. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48:3486–3494. - PubMed
-
- Müller S., Frosch K.H., Frings J., Berninger M., Krause M. Biplanar high tibial osteotomy for the combined correction of varus and posterior tibial slope malalignment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023;109 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

