Prognostic value of inflammatory markers and different treatment regimens in neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma: a retrospective study
- PMID: 40822489
- PMCID: PMC12354512
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1652092
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers and different treatment regimens in neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma (NECC) is a rare and highly aggressive gynecological tumor, with poor prognosis and limited standardized treatment options. Inflammation plays a significant role in tumor progression, and systemic inflammatory markers such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) have shown prognostic value in other malignancies. However, their role in NECC remains unclear.
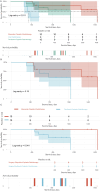
Methods: This single-center retrospective study included 25 NECC patients treated at our hospital between 2014 and 2024. Patients were divided into three groups based on treatment regimens: paclitaxel plus cisplatin combined with radiotherapy, etoposide plus cisplatin combined with radiotherapy, and radiotherapy alone. Baseline characteristics, inflammatory markers, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Log-rank tests were used to compare survival differences.
Results: The median survival time was significantly longer in the etoposide plus cisplatin plus radiotherapy group (1,000 days) compared to the paclitaxel plus cisplatin plus radiotherapy group (776 days) and the radiotherapy-alone group (347 days, P = 0.037). The radiotherapy-alone group had significantly higher neutrophil counts (median = 5.46 × 109/L, P = 0.006), platelet counts (median = 282.5 × 109/L, P = 0.017), NLR (median = 4.68, P < 0.05), and PLR (median = 231.93, P < 0.05), while LMR (median = 1.89, P < 0.05) was lower. For postoperative patients, the median survival time was 1,453 days for the surgery plus etoposide plus cisplatin plus radiotherapy group, compared to 987 days for the surgery plus paclitaxel plus cisplatin plus radiotherapy group (P = 0.048).
Conclusion: Combined chemotherapy with etoposide plus cisplatin and radiotherapy significantly improves survival outcomes in NECC patients compared to radiotherapy alone. This regimen may be particularly beneficial for postoperative patients and those with high-risk factors such as lymphovascular space invasion. Further studies are needed to validate these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols for NECC.
Keywords: clinical research; inflammatory markers; neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma; prognosis; retrospective study.
Copyright © 2025 Kuang, Wang, Yu, Shen, Peng, Li, Cheng and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of different treatment modalities for the management of adult-onset granulosa cell tumours of the ovary (primary and recurrent).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 21;2014(4):CD006912. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006912.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24753008 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Hysterectomy with radiotherapy or chemotherapy or both for women with locally advanced cervical cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 7;(4):CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub3. PMID: 25847525 Updated.
References
-
- Bellone S., Jeong K., Halle M. K., Krakstad C., McNamara B., Greenman M., et al. (2024). Integrated mutational landscape analysis of poorly differentiated high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121, e2321898121. 10.1073/pnas.2321898121 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budin C. E., Cocuz I. G., Enache L. S., Rența I. A., Cazacu C., Pătrîntaşu D. E., et al. (2024). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio: side by side with molecular mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer-the INOLUNG study. Cancers (Basel) 16, 2903. 10.3390/cancers16162903 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

