Exploring the pathogenesis of acute lung injury and its treatment through Traditional Chinese Medicine: a state-of-the-art review
- PMID: 40822495
- PMCID: PMC12351183
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1592458
Exploring the pathogenesis of acute lung injury and its treatment through Traditional Chinese Medicine: a state-of-the-art review
Abstract
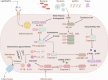
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) is a severe and progressive condition characterized by hypoxic respiratory failure, often triggered by multiple contributing factors. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates and can advance to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in severe cases. The pathogenesis of ALI involves a complex interplay of pathological mechanisms, including immune-inflammatory responses, disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier, damage to mesenchymal stem cell organelles, metabolic dysregulation, ferroptosis, and alterations in gut microbiota. From the perspective of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the development of ALI is primarily attributed to the invasion of toxic pathogens, which result in lung dysfunction. TCM treatment strategies, which emphasize heat-clearing, detoxification, promoting blood circulation, and resolving stasis, have demonstrated promising clinical efficacy. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the pathogenesis of ALI and explores the therapeutic mechanisms of TCM compounds and bioactive monomers with potential therapeutic benefits. The goal is to establish a solid theoretical foundation for the clinical application of TCM in ALI treatment and to further validate its scientific rationale.
Keywords: Traditional Chinese Medicine; acute lung injury; bioactive compounds; pathogenesis; treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Yan, Zhang, Wang, Jiao, Zhu, Tan and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Targeting ferroptosis using Chinese herbal compounds to treat respiratory diseases.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul 25;130:155738. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155738. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38824825
-
Investigation of the effect and mechanism of Fei Re Pu Qing powder in treating acute lung injury (ALI) by modulating macrophage polarization via serum pharmacology and network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120089. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120089. Epub 2025 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40499803
-
Targeting ferroptosis in the treatment of ulcerative colitis by traditional Chinese medicine: A novel therapeutic strategies.Phytomedicine. 2025 Apr;139:156539. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156539. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39987602
-
To explore pharmacodynamic substances and mechanism of Xuanfei Baidu Decoction on LPS-induced ALI / ARDS by pharmacochemistry and metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;338(Pt 2):119043. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119043. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39515677
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources