Individuals Recovered from Severe COVID-19 are Predispose to Develop Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 40822898
- PMCID: PMC12357568
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S527058
Individuals Recovered from Severe COVID-19 are Predispose to Develop Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Aim: One of the primary contributors of the development of atrial fibrillation (AF) is autonomic dysfunction. It is suggested that heart rate turbulence (HRT) be utilized to assess autonomic nervous system (ANS) function. In this research, we analyzed the impact of COVID-19 on atrial fibrillation predisposition in the post-recovery period by analyzing atrial HRT measurements of patients who described palpitations in the post-COVID-19 period.
Methods: This study included 407 healthy participants without a positive COVID-19 record and 328 patients having a verified positive COVID-19 record (recovered COVID-19). All subjects were categorized into four groups (controls, recovered mild COVID-19, recovered moderate COVID-19 and recovered severe COVID-19) based on the severity value of their chest CT scan. The atrial HRT analyses were taken from a 24-hour electrocardiography- Holter recording.
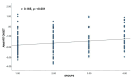
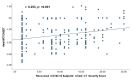
Results: This study revealed that atrial HRT Onset values were significantly higher in the recovered severe COVID-19 group than the other groups. A positive association was found between the atrial HRT onset value and the chest CT severity value. However, no relationship was found between the atrial HRT onset value and the number of positive PCR test for COVID-19 or the amount of time that had passed since COVID-19. Regression analysis showed that the chest CT severity score, HT, smoking, and recovery from severe COVID-19, were independent predictors of atrial HRT Onset values and abnormal atrial HRT Onset existence.
Conclusion: Blunted atrial HRT, considered a significant predisposition to the development of atrial fibrillation, is more likely to occur in people who recovered from serious COVID-19 than in individuals who have never had severe COVID-19. These individuals should be carefully evaluated for atrial HRT.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; atrial heart rate turbulence; autonomic nervous system disorder; recovery from severe COVID-19.
© 2025 Yılmaz and Mirzaoğlu.
Conflict of interest statement
Regarding the research, authorship, and/or publishing of this paper, the authors have no possible conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Demirhan R, Çimenoğlu B, Yılmaz E. The effects of hospital organization on treatment during COVID-19 pandemic. South Clin Ist Euras. 2020;31:89–95 doi: 10.147/scie.2020.32154 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

