Diode Laser Treatment for Buccal Mucosa Fibrolipoma in an Elderly Patient on Anticoagulants: Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 40822912
- PMCID: PMC12356663
- DOI: 10.1155/crid/8847648
Diode Laser Treatment for Buccal Mucosa Fibrolipoma in an Elderly Patient on Anticoagulants: Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
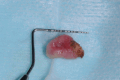
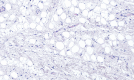
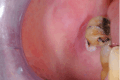
Introduction: Lipomas are benign neoplasms originating from mesenchymal soft tissue, primarily composed of mature adipocytes and surrounded by a fibrous capsule. While they are relatively common in the head and neck region, oral cavity involvement is rare. Fibrolipoma (FL) is a variant characterized by lobules of adipocytes with dense collagen bands. Its etiology remains uncertain and can occasionally be found in the buccal mucosa. Surgical excision is the gold standard for oral lipomas, and the prognosis is generally favorable. This case report describes the excision of a buccal mucosa FL in a 92-year-old patient undergoing anticoagulant therapy using a diode laser. Methods: A 92-year-old patient with a medical history of benign prostatic hyperplasia and hypertension, under anticoagulant therapy, presented with a painless buccal mucosa swelling. The growth affected both the superficial and submucosal layers. Surgical removal of the FL using a diode laser was performed. Results: The diode laser excision of the FL was carried out successfully, with immediate cauterization, eliminating the need for sutures or hemostatic agents. Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of FL. Postoperative healing was uneventful at both 1- and 3-month follow-ups. Conclusions: Oral FLs are rare benign tumors primarily treated through surgical excision. In this case, the use of a diode laser provided effective hemostasis, minimal scarring, and rapid recovery, making it a suitable option for patients under anticoagulant therapy. While this report presents promising results, further cases with longer follow-up periods are needed to establish the effectiveness and safety of this technique. Laser technology continues to emerge as a valuable tool in oral pathology and surgery, offering minimally invasive alternatives to traditional approaches.
Keywords: buccal mucosa; dentistry; diode laser; laser surgery; oral fibrolipoma; oral pathology.
Copyright © 2025 Matteo Pellegrini et al. Case Reports in Dentistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Single-Stage Pedicle Preputial Tube Substitution Urethroplasty with Corpora Cavernosa Augmentation Using Buccal Mucosa Graft for Primary Peno-Scrotal Hypospadias Re-pair in Adults.Int Braz J Urol. 2025 Jul-Aug;51(4):e20240650. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2024.0650. Int Braz J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40105707 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoral Lipoma on the Palate of an 11-Year-Old Patient: A Case Report.Reports (MDPI). 2025 Feb 8;8(1):19. doi: 10.3390/reports8010019. Reports (MDPI). 2025. PMID: 40729232 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- de Visscher J. G. Lipomas and Fibrolipomas of the Oral Cavity. Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery . 1982;10(3):177–181. - PubMed
-
- Studart-Soares E. C., Costa F. W., Sousa F. B., Alves A. P., Osterne R. L. Oral Lipomas in a Brazilian Population: A 10-Year Study and Analysis of 450 Cases Reported in the Literature. Medicina Oral, Patología Oral y Cirugía Bucal . 2010;15(5):e691–e696. - PubMed
-
- Gnepp D. R., editor. Diagnostic Surgical Pathology of the Head and Neck . WB Saunders; 2001.
-
- Weiss S. W., Goldblum J. R., editors. Enzinger and Weiss’s Soft Tissue Tumors . Elsevier; 2001. Benign Lipomatous Tumors; pp. 571–639.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

