Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- PMID: 40822969
- PMCID: PMC12355368
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2025-1131
Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
Abstract
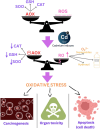
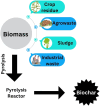
Cadmium induces toxicity to both flora and fauna, even when it is present in trace amounts. Electroplating, pigments, smelting, mining, alloy production, plastic, cadmium-nickel batteries, fertilizers, pesticides, paint, synthesis of dye, textile operations, and refining sectors all release cadmium into the aquatic environment. "Solvent extraction, adsorption, ion exchange, and precipitation" are a few strategies for removing cadmium. Biochar is an inexpensive and sustainable adsorbent that has proven to be an efficacious adsorbent for the recovery of Cd(ii) from water. This study discusses the toxicity of cadmium as well as some recent developments of pristine biochar and modified biochar for the elimination of cadmium (Cd) from aqueous solution.
Keywords: adsorption; biochar; cadmium; mechanism; water treatment.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Revitalizing cadmium-stressed sunflower: co-composted biochar improves growth, antioxidant responses, and soil remediation efficiency.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):875. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06906-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40615980 Free PMC article.
-
Biochar-based catalysts: an efficient and sustainable approach for water remediation from organic pollutants via advanced oxidation processes.J Environ Manage. 2025 Aug;390:126245. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.126245. Epub 2025 Jun 21. J Environ Manage. 2025. PMID: 40544812 Review.
-
Simultaneous remediation of As(V), Cd(II) and Pb(II) in aqueous solution and soil using Fe/Ca-modified biochar.Waste Manag Res. 2025 Aug;43(8):1206-1218. doi: 10.1177/0734242X241307521. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Waste Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40746064 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saraeian A, Hadi A, Raji F, Ghassemi A, Johnson M. Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by low-cost native and surface modified Sorghum x drummondii (Sudangrass). J Environ Chem Eng. 2018 Apr;6(2):3322–31. Satarug, S. and Moore, M.R., Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environmental health perspectives, 2004, 112(10), 1099–1103. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Subrahmanyam G, Mondal R, Cabral-Pinto MM, Shabnam AA, Jigyasu DK, et al. Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere. 2021 Apr;268:128855. - PubMed
-
- United states environmental protection agency (USEPA). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. Washington, DC, USA: USEPA; 2019.
-
- Vardhan KH, Kumar PS, Panda RC. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J Mol Liq. 2019 Sep;290:111197.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
