Composite dietary antioxidant index and HPV infection from single and mixed associations to SHAP-interpreted machine learning predictions
- PMID: 40823022
- PMCID: PMC12350107
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1619742
Composite dietary antioxidant index and HPV infection from single and mixed associations to SHAP-interpreted machine learning predictions
Abstract
Background: Some studies have shown that dietary antioxidants may prevent the occurrence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection. However, the relationship between the composite dietary antioxidant index (CDAI) and HPV infection among adult women in the United States remains unknown.
Methods: Participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 2003-2016 were included. Multivariable logistic regression, restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression, weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression, and Bayesian kernel machine regression (BKMR) were used to analyze the associations between CDAI and its sub-components and HPV infection. In addition, nine machine learning (ML) methods were employed to construct predictive models, and SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) was used to further interpret the optimal model.
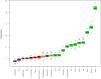
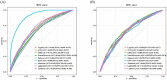
Results: This study enrolled 9,224 adult female participants. After adjusting for multiple confounding variables, CDAI was independently negatively associated with HPV infection (OR: 0.98, 95%CI: 0.97-0.99, p = 0.01). RCS indicated an L-shaped association between CDAI and HPV infection. In the WQS model, the WQS index of CDAI was still robustly negatively associated with HPV infection (OR: 0.78, 95%CI: 0.71-0.86, p < 0.0001). In the mixture effect, BKMR analysis confirmed the negative association between six antioxidants and HPV infection. Both WQS and BKMR confirmed that vitamin E had the strongest negative association with HPV infection. Additionally, among the nine machine-learning models, the Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) showed the best predictive performance [area under curve (AUC) = 0.685]. SHAP analysis indicated that marital status, smoking, drinking, race, age, and CDAI had a significant impact on the model's prediction.
Conclusion: Antioxidant-rich diets, especially increased intake of vitamin E, are significantly negatively associated with HPV infection. A GBM model with 12 features can effectively predict the occurrence of HPV infection, among which CDAI is an important factor in the model.
Keywords: BKMR; HPV infection; NHANES; SHAP; WQS; composite dietary antioxidant index; machine learning.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The relationship between flavonols intake and stroke in the elderly: a cross-sectional study from NHANES (2007-2010 and 2017-2018).J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2025 Aug;34(8):108373. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2025.108373. Epub 2025 Jun 7. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40490174
-
Association Between Composite Dietary Antioxidant Index and Pregnancy: Insights from the NHANES.Reprod Sci. 2025 Jul;32(7):2362-2374. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01905-8. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40550984
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonjour M, Charvat H, Franco EL, Piñeros M, Clifford GM, Bray F, et al. Global estimates of expected and preventable cervical cancers among girls born between 2005 and 2014: a birth cohort analysis. Lancet Public Health. (2021) 6:e510–21. doi: 10.1016/s2468-2667(21)00046-3, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

