Oxidative stress-related genes in uveal melanoma: the role of CALM1 in modulating oxidative stress and apoptosis and its prognostic significance
- PMID: 40823088
- PMCID: PMC12353749
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1618601
Oxidative stress-related genes in uveal melanoma: the role of CALM1 in modulating oxidative stress and apoptosis and its prognostic significance
Abstract
Background: Uveal melanoma (UVM) is a rare yet aggressive form of ocular cancer with a poor prognosis. This study aims to investigate the role of oxidative stress-related genes (OSGs) in UVM, focusing on their involvement in key signaling pathways and immune infiltration and their potential as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
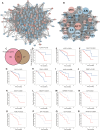
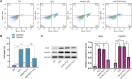
Method: Differential gene expression analysis was conducted using 175 samples of normal retinal pigmented epithelium-choroid complex samples and 63 samples from UVM. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks were constructed to identify hub genes, and machine learning algorithms were utilized to screen for diagnostic genes, employing methods such as least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, random forest, support vector machine (SVM), gradient boosting machine (GBM), neural network algorithm (NNET), and eXtreme gradient boosting (XGBoost). A risk signature model was developed using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort and validated using the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC), GSE84976 dataset. Clinical samples were used to validate the diagnostic value. Experimental validation encompassed H2O2-induced oxidative stress assays and CALM1 overexpression analysis in UVM cells to evaluate its protective effects.
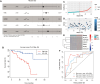
Results: A total of 2,576 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, with 185 overlapping OSGs enriched in pathways such as HIF-1, FoxO, PI3K-Akt, and apoptosis. Prognostic hub OSGs, including ACACA, CALM1, and DNM2, were associated with poor survival outcomes in the training set and multiple validation data. Revalidation using clinically collected samples confirmed that CALM1 exhibits superior diagnostic value. The risk signature model demonstrated strong predictive accuracy for a 5-year overall survival (AUC = 0.844). Immune infiltration analysis revealed increased CD4+ memory-activated T cells and mast resting cells in the high-risk group. Additionally, CALM1 overexpression attenuated H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in UVM cells. CALM1 upregulation also mitigated the inhibitory effects of H2O2 on key cellular processes, including proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: This study underscores the critical role of OSGs in the progression of UVM and their potential as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. The identified risk signature model and the protective role of CALM1 offer valuable insights for developing targeted therapies and enhancing patient clinical outcomes in UVM.
Keywords: CALM1; machine learning algorithms; oxidative stress; risk signature; uveal melanoma.
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Cai, Hu, Cao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Machine learning based screening of biomarkers associated with cell death and immunosuppression of multiple life stages sepsis populations.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14600-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830558 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a lipid metabolism-related genes prognostic signature for skin cutaneous melanoma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Aug 15;775:152115. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152115. Epub 2025 May 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40460484
-
A newly developed ferroptosis-related gene signature for forecasting prognosis in uveal melanoma.Methods. 2025 Oct;242:187-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2025.08.001. Epub 2025 Aug 6. Methods. 2025. PMID: 40763838
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oxenreiter MM, Lane AM, Aronow MB, Shih H, Trofimov AV, Kim IK, et al. Proton beam irradiation of uveal melanoma involving the iris, ciliary body and anterior choroid without surgical localisation (light field). Br J Ophthalmol. (2022) 106:518–21. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-318063, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

