Beliefs about causes of cancer among students around the world
- PMID: 40823099
- PMCID: PMC12353720
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1631997
Beliefs about causes of cancer among students around the world
Abstract
Introduction: Early prevention, especially among young adolescence, could reduce cancer incidence. The aim of the study was to assess beliefs on cancer risk factors among students.
Material and methods: The study was conducted among 761 Polish students and 140 students from 32 other countries. The study was provided using an original, validated questionnaire.
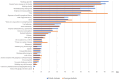
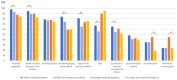
Results: The most commonly indicated cancer risk factors by both Polish and foreign students were smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol, sunbathing/using tanning beds, exposure to ionizing radiation, diet, and exposure to harmful occupational factors. There is a gap in knowledge concerning some other risk factors: low physical activity, viral infection, and hormonal contraception. Students indicated genetic factors and smoking as a main cancer causes. Medical students were more aware of different cancer risk factors compared with non-medical students. Nationality (Polish/foreign), medical field of study, female, having cancer patient among friends/family, and living in bigger city were significantly associated with beliefs about different cancer risk factors.
Conclusion: Medical students demonstrated better knowledge about cancer causes than non-medical students, but it seems that the genetic factor is overestimated by students. It is necessary to provide education even among teenagers to increase cancer prevention. Special attention in raising awareness should be paid to cancer risk factors of physical inactivity and viral infection.
Keywords: cancer prevention; cancer risk factors; genetic factors; lifestyle; students.
Copyright © 2025 Bordakiewicz, Pokorska, Cieniawa, Mikołajczyk, Mikołajczyk, Rucińska and Osowiecka.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dattani S, Samborska V, Ritchie H, Roser M. Cancer. Oxford, UK: Our World in Data; (2024). Available online at: https://ourworldindata.org/cancer.
-
- OECD . Tackling the impact of cancer on health, the economy and society (2024). Available online at: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/tackling-the-impact-of-cancer-on-he... (Accessed March 1, 2025).
-
- Nowotwory złośliwe w Polsce . Krajowy rejestr nowotworów (2022). Available online at: https://onkologia.org.pl/pl/epidemiologia/nowotwory-zlosliwe-w-polsce (Accessed March 1, 2025).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous