Formation of different flavor characteristics of raw- and boiled-dried oysters
- PMID: 40823135
- PMCID: PMC12355567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102854
Formation of different flavor characteristics of raw- and boiled-dried oysters
Abstract
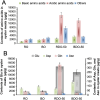
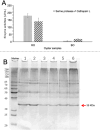
The release of flavor compounds in dried oysters, particularly umami amino acids, is highly dependent on the proteolytic degradation efficiency of specific targeted proteins, which is critically influenced by processing techniques. However, systematic studies on this mechanism remain scarce. This study elucidated how processing techniques govern flavor formation in dried oysters. Mild drying 50 °C in raw oysters triggered intense protein degradation, increasing glutamic acid and maximizing umami intensity, but accumulated bitter compounds. Conversely, 90 °C drying suppressed bitterness yet reduced umami and caused extreme yellowing. Mass spectrometry revealed that hydrophilic domains in ∼35 kDa oyster proteins (mainly glutamic acid-rich proteins, such as β-tubulin chain and actin-like proteins) were enzymatically targeted, releasing free glutamic acid as the core umami contributor. This work demonstrated the synergistic effects of pre-cooking and temperature on flavor, and findings provide a scientific basis for optimizing dried oyster processing.
Keywords: Dried oyster; Flavor formation; Glutamic acid release; Protein degradation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ahmed Z., Donkor O., Street W.A., Vasiljevic T. Calpains- and cathepsins-induced myofibrillar changes in post-mortem fish: Impact on structural softening and release of bioactive peptides. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2015;45(1):130–146. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.04.002. - DOI
-
- Ajandouz E.H., Desseaux V., Tazi S., Puigserver A. Effects of temperature and pH on the kinetics of caramelisation, protein cross-linking and Maillard reactions in aqueous model systems. Food Chemistry. 2008;107(3):1244–1252. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.062. - DOI
-
- Benjakul S., Singh A., Sae-Leaw T., Balange A.K. Endogenous enzymes: Their roles in quality of fish/shellfish and their products. Advances in Fish Processing Technologies. 2023:235–269. doi: 10.1201/9781003300595-13. - DOI
-
- Bonazzi C., Dumoulin E. Quality changes in food materials as influenced by drying processes. Modern drying technology. 2011;3:1–20. doi: 10.1002/9783527631667.ch1. - DOI
-
- Cheng S., Zhang T., Yao L., Wang X., Song Y., Wang H., Tan M. Use of low-field-NMR and MRI to characterize water mobility and distribution in pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) during drying process. Drying Technology. 2017;36(5):630–636. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2017.1359839. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

