Structured detection for simultaneous super-resolution and optical sectioning in laser scanning microscopy
- PMID: 40823346
- PMCID: PMC12353846
- DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01695-0
Structured detection for simultaneous super-resolution and optical sectioning in laser scanning microscopy
Abstract
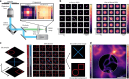
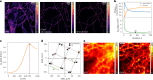
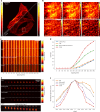
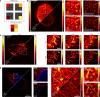
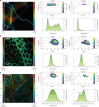
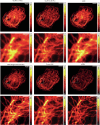
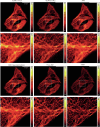
Fast detector arrays enable an effective implementation of image scanning microscopy, which overcomes the trade-off between spatial resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of confocal microscopy. However, current image scanning microscopy approaches do not provide optical sectioning and fail with thick samples unless the detector size is limited, thereby introducing a new trade-off between optical sectioning and signal-to-noise ratio. Here we propose a method that overcomes such a limitation. From single-plane acquisition, we reconstruct an image with digital and optical super-resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio and enhanced optical sectioning. On the basis of the observation that imaging with a detector array inherently embeds axial information, we designed a straightforward reconstruction algorithm that inverts the physical model of image scanning microscopy image formation. We present a comprehensive theoretical framework and validate our method with images of biological samples captured using a custom setup equipped with a single-photon avalanche diode array detector. We demonstrate the feasibility of our approach by exciting fluorescence emission in both linear and nonlinear regimes. Moreover, we generalize the algorithm for fluorescence lifetime imaging, fully exploiting the single-photon timing ability of the single-photon avalanche diode array detector. Our method outperforms conventional reconstruction techniques and can be extended to any laser scanning microscopy technique.
Keywords: Fluorescence imaging; Imaging and sensing; Super-resolution microscopy.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsG.V. has a personal financial interest (co-founder) in Genoa Instruments, Italy. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
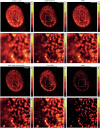
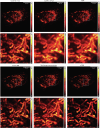
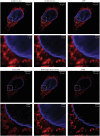
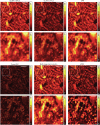
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Plug-and-play algorithm for 3D guided video super-resolution of single-photon LiDAR data.Opt Express. 2025 Mar 10;33(5):11775-11792. doi: 10.1364/OE.550516. Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40798789
-
Texture features-guided image reconstruction kernel method for18F-FDG delayed PET imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2025 Jul 17;70(14). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/adee74. Phys Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40639403
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Mertz, J. Optical sectioning microscopy with planar or structured illumination. Nat. Methods8, 811–819 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Macias-Garza, F., Bovik, A. C., Diller, K. R., Aggarwal, S. J. & Aggarwal, J. K. The missing cone problem and low-pass distortion in optical serial sectioning microscopy. IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Process.2, 890–893 (1988).
-
- Mertz, J. Introduction to Optical Microscopy 2nd edn (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2019).
-
- Huisken, J., Swoger, J., Bene, F. D., Wittbrodt, J. & Stelzer, E. H. K. Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy. Science305, 1007–1009 (2004). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
