Prediction of mechanical complications post-acute myocardial infarction in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40823548
- PMCID: PMC12355605
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1635357
Prediction of mechanical complications post-acute myocardial infarction in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represent a unique population characterized by poorer prognoses, which may be further exacerbated by mechanical complications. This study aims to develop a predictive model to identify high-risk individuals within this populations.
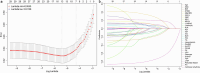
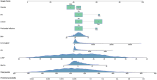
Methods: This study enrolled AMI patients with T2DM and categorized them into complication and control groups. The mechanical complications were defined as papillary muscle rupture (with or without acute mitral regurgitation), ventricular septal defect, left ventricular pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (with or without thrombus) and free wall rupture. Characteristics were selected using relaxed least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression, multivariate logistic regression and random forest model. Selected variables were utilized to construct a nomogram to predict the possibility of mechanical complications.
Results: A total of 2,816 patients were enrolled, with 191 individuals classified into the complication group. Baseline analysis identified 31 factors exhibiting potential differences, which were subsequently employed for LASSO-logistic regression, multivariate logistic regression and random forest model. After comprehensive evaluation, nine variables emerged as predictive factors for mechanical complications, including gender, pulmonary hypertension, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, body mass index, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, creatine kinase, left ventricle ejection fraction and hemoglobin A1c, which were used to construct a reliable nomogram. The complication group also showed higher in-hospital mortality rates compared to controls, alerting the worse prognosis of these populations.
Conclusion: This study identified nine factors upon admission that may be associated with mechanical complications during the hospitalization. A nomogram was developed based on these factors for clinical application. T2DM patients should emphasize glucose control, which may offer benefits following the onset of AMI.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; hemoglobin A1c; mechanical complications; prediction model; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Wang, Yuan and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang H, Xie X, Zu Q, Lu M, Chen R, Yang Z, et al. Treatment of the new era: Long-term Ticagrelor monotherapy for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following percutaneous coronary intervention: a Meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. (2023) 14:47–61. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01350-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

