Association of increased serum I-309 with renal function impairment and diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40823933
- PMCID: PMC12400501
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-25-0252
Association of increased serum I-309 with renal function impairment and diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine serum I-309 levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, as well as the association with clinical/laboratory phenotypes and disease complications.
Methods: A total of 155 T2DM patients and 30 healthy controls (HC) were enrolled. The concentrations of serum I-309, interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17, IL-23, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferon (IFN)-γ were measured. The relationships between I-309 and various clinical and laboratory variables were analyzed.
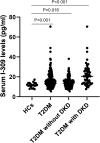
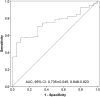
Results: The serum concentrations of I-309 were significantly higher in T2DM patients than in HC (P < 0.001). The serum I-309 levels were significantly elevated in T2DM patients with diabetic kidney disease (DKD), hypertension, coronary artery disease, peripheral neuropathy, peripheral artery disease, and diabetic ketosis (all P < 0.05), but reduced in drinkers (P = 0.018). The Spearman analysis showed that serum I-309 correlated positively with age, disease duration, CKD stages, urea, creatinine, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio, C-reactive protein, red blood cell distribution width, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, IL-6, IL-12, and IFN-γ, but negatively with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), fasting blood glucose, total bilirubin, albumin, lymphocyte count, red blood cell count, and hemoglobin. The multiple linear regression analysis indicated that serum I-309 was independently correlated only with eGFR and IFN-γ. The multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that serum I-30 and IL-17A remained independently associated with DKD.
Conclusion: Serum I-309 is markedly elevated in T2DM patients and is associated with increased DKD risk, suggesting its potential role as both a promising biomarker and a pathogenic mediator in the progression of T2DM, particularly DKD.
Keywords: I-309; diabetic kidney disease; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the work reported.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous