Transcranial ultrasound in the critically ill patient: a narrative review
- PMID: 40824473
- PMCID: PMC12361031
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-025-00787-z
Transcranial ultrasound in the critically ill patient: a narrative review
Abstract
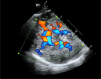
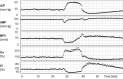
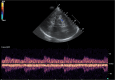
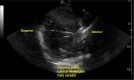
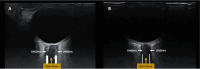
Transcranial ultrasound is gaining widespread recognition as a useful bedside monitoring tool and non-invasive diagnostic device in the critically ill patient. The capabilities of transcranial ultrasound are themselves ever-increasing, and this, combined with improved physiological understanding, affords insights into pathophysiological processes often concealed from the bedside critical care clinician. Transcranial ultrasound remains unique in regard to its non-invasive, rapid, and critically composite blood flow velocity-centric (not pressure-centric) information. The mobility of transcranial ultrasound devices is of particular value to the largely immobile critically ill patient requiring multiple organ supportive therapies. In this review, we discuss some important origins of more modern composite techniques and highlight relevant major key concepts, whilst noting exciting frontier possibilities.
Keywords: Critical care; Doppler ultrasonography; Doppler ultrasound imaging; Intensive care; Point-of-care diagnostics; Transcranial.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Not required for this manuscript. Consent for publications The manuscript has been reviewed and approved by both authors who consent for publication. Competing interests: RMJC—nil conflict of interest to declare, MC—receives licensing fee for ICM + (Cambridge Enterprise Ltd). MC has received honoraria from Integra LifeScience as a speaker and Delica Ltd (China). The manuscript has not been published or submitted for publication elsewhere.
Figures



References
-
- Leksell L (1956) Echo-encephalography. I. Detection of intracranial complications following head injury. Acta Chir Scand 110(4):301–315 - PubMed
-
- Furuhata H (1989) A new evolution of transcranial tomography (TCT) and transcranial Doppler Tomography (TCDT). Neurosonology 2:8–15
-
- Aaslid R, Markwalder TM (1982) Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 57(6):769–774. 10.3171/jns.1982.57.6.0769 - PubMed
-
- Bartels E (2002) The axial imaging plane—the main domain of the transcranial color-coded duplex ultrasonography? Eur J Ultrasound 16(1–2):47–57. 10.1016/S0929-8266(02)00067-8 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

