Antibacterial activity of promising nanostructured cesium oxide
- PMID: 40824504
- PMCID: PMC12360994
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-025-04327-2
Antibacterial activity of promising nanostructured cesium oxide
Abstract
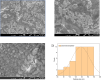
As bacterial strains become increasingly resistant to antibiotics, many researchers are seeking novel, effective, and inexpensive antibiotics. Some nanomaterials have been suggested as potential candidates for use as novel antibacterial agents. In this study, cesium oxide nanoparticles were synthesized and preliminarily investigated for their ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria. Although there are few studies on the applications of cesium oxide, it is possible that this oxide could have a substantial impact on biological activities. Cesium oxide nanoparticles were synthesized via fast calcination at 500 °C for 3 h. The composition and morphology of the prepared samples were characterized via X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscope analysis, which verified the synthesis of cesium oxide nanoparticles. Agar well diffusion and minimum inhibitory concentration assays were used to study the antibacterial activity of cesium oxide nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The experimental results provide preliminary support for developing cesium oxide nanostructures as antibacterial agents against a wide range of infections and diseases caused by bacteria.
Keywords: Agar well diffusion; Antibacterial activity; Calcination; Cesium oxide; Minimum inhibitory concentration; Nanoparticles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Biological activities of optimized biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using Proteus mirabilis PQ350419 alone or combined with chitosan and ampicillin against common multidrug-resistant bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jul 5;24(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02783-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40618114 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Hypericum perforatum L. and Their Effects on Staphylococcus aureus.Microsc Res Tech. 2025 Aug;88(8):2321-2332. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24862. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Microsc Res Tech. 2025. PMID: 40121669 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Ferraz MP. Antimicrobial resistance: the impact from and on society according to one health approach. Societies. 2024;14(9):1–22. 10.3390/soc14090187.
-
- World Health Organization. 10 global health issues to track in 2021. 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/10-global-health-issues-to-track...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
