Identifying trends in reporting on the ethical treatment of insects in research
- PMID: 40824963
- PMCID: PMC12360591
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328931
Identifying trends in reporting on the ethical treatment of insects in research
Abstract
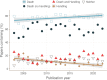
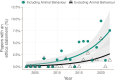
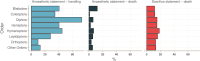
Transparent reporting on the ethical treatment of research animals (e.g., implementation of the 3Rs, replace, reduce, and refine) is recommended when publishing in peer-reviewed literature. This is meant to foster public trust, safeguard animal welfare, and generate reproducible science. However, entomologists are not expected to engage in such reporting, as their research is not subject to legislated ethical review. Recently, however, entomologists have reported increased concern about the ethical treatment of insects in research, and associated reproducibility and public trust issues. To what degree are these increasing concerns reflected in changes in practices? We surveyed 15 high-impact journals that publish on insects over 20 years to collect data on reporting related to the ethical treatment of insects in research, including animal reduction methods, analgesics/anesthesia statements, and information regarding sacrifice. Out of 1359 sampled papers, no studies reported any methods to reduce animal use. Over 20 years, we found an increase in the proportion of papers reporting insect death and a decrease in the papers reporting significant invasive handling. 84% of papers with significant animal handling or death did not report the use of any anesthetics. We also found an increase in animal-treatment-specific ethics statements (from 0% to 8%), largely driven by the journal Animal Behaviour. We end by 1) making recommendations for entomologists looking to improve their reporting practices and 2) providing tools to improve transparent reporting of information related to the ethical treatment of insects in research.
Copyright: © 2025 Perl et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
MB and BF report a relationship with the Insect Welfare Research Society that includes: board of advisors (unpaid). CDP reports a relationship with the Insect Welfare Research Society that includes: employment. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Do peer reviewers comment on reporting items as instructed by the journal? A secondary analysis of two randomized trials.J Clin Epidemiol. 2025 Jul;183:111818. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2025.111818. Epub 2025 May 8. J Clin Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40348145
-
Interventions for preventing and reducing the use of physical restraints for older people in all long-term care settings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 28;7(7):CD007546. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007546.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37500094 Free PMC article.
-
Individual-level interventions to reduce personal exposure to outdoor air pollution and their effects on people with long-term respiratory conditions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 9;8(8):CD013441. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013441.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34368949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eisemann CH, Jorgensen WK, Merritt DJ, Rice MJ, Cribb BW, Webb PD, et al. Do insects feel pain? — A biological view. Experientia. 1984;40(2):164–7. doi: 10.1007/bf01963580 - DOI
-
- Can insects feel pain? A review of the neural and behavioural evidence. Advances in Insect Physiology. Elsevier. 2022. p. 155–229. doi: 10.1016/bs.aiip.2022.10.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

