Is There a Role for Mifamurtide in Nonmetastatic High-Grade Osteosarcoma? Results From the Italian Sarcoma Group (ISG/OS-2) and Spanish Sarcoma Group (GEIS-33) Trials
- PMID: 40825172
- PMCID: PMC12456199
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-00210
Is There a Role for Mifamurtide in Nonmetastatic High-Grade Osteosarcoma? Results From the Italian Sarcoma Group (ISG/OS-2) and Spanish Sarcoma Group (GEIS-33) Trials
Abstract
Purpose: Outcome of patients with localized osteosarcoma is challenging. The role of mifamurtide is still a matter of debate. Two prospective trials were carried out in Italy (ISG/OS-2) and Spain (GEIS-33) with mifamurtide in ABCB1/P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-positive patients.
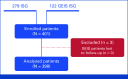
Patients and methods: Patients age ≤40 years with localized extremity high-grade osteosarcoma were eligible. Analysis of Pgp expression from diagnostic biopsy was centralized. Patients received two cycles of preoperative methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatinum (MAP) before surgery. Postoperatively, in case of Pgp overexpression (Pgp-positive), mifamurtide was added, combined with doxorubicin (one cycle) and four consecutive cycles of high-dose ifosfamide (HDIFO) for patients with poor histologic response, or with MAP in case of good response. Patients who were Pgp-negative received MAP postoperatively. We present the merged analysis of ISG/OS-2 and GEIS-33 trial, an observational study with same inclusion criteria and treatment of ISG/OS-2. The primary endpoint was 5-year event-free survival (EFS) according to the use of mifamurtide. Secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS).
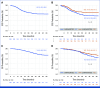
Results: From March 2013 to April 2018, 398 patients were analyzed. The median age was 14 years (range, 4-40), male/female: 238/160 (1.48/1.0); 211 of 398 (53%) tumors were Pgp-positive, and 204 of 398 (51.3%) patients received mifamurtide. With a median follow-up of 70 months (IQR, 49-90 months), the 5-year EFS and OS were 65.2% (95% CI, 60.1 to 69.8) and 74.8% (95% CI, 69.8 to 79.0), respectively, with superior EFS for patients undergoing mifamurtide and chemotherapy as compared with EFS of patients undergoing chemotherapy alone (5-year EFS 71.4% v 58.3%; P = .0139) not confirmed at multivariable analysis (P = .0593).
Conclusion: In this merged analysis with a risk-adapted strategy for nonmetastatic osteosarcoma, the group with unfavorable prognoses, identified by Pgp expression, performed well when mifamurtide, combined with HDIFO in case of poor response, was administered after surgery.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04383288 NCT01459484.
Conflict of interest statement
Is There a Role for Mifamurtide in Nonmetastatic High-Grade Osteosarcoma? Results From the Italian Sarcoma Group (ISG/OS-2) and Spanish Sarcoma Group (GEIS-33) Trials
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures




References
-
- Gitelis S. Bone and soft tissue tumors: Clinical features, imaging, pathology and treatment. 2nd ed. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83:801–802.
-
- Baumhoer D, Böhling TO, Cates JMM, et al. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020. Osteosarcoma, in WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (ed): Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, Volume 3 (ed 5) pp. 403–409.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

