Optimizing the Postcataract Patient Journey Using AI-Driven Teleconsultation: Prospective Case Study
- PMID: 40825199
- PMCID: PMC12360671
- DOI: 10.2196/72574
Optimizing the Postcataract Patient Journey Using AI-Driven Teleconsultation: Prospective Case Study
Abstract
Background: Given the increasing global demand for ophthalmologic care and the anticipated shortage of ophthalmology professionals, innovative solutions are essential for optimizing health care delivery. Digital health technologies offer promising opportunities to efficiently manage high patient volumes. Cataract surgery, with its established safety profile and routine postoperative care, provides an ideal setting for implementing such innovations. Structured clinical questions have proven effective in identifying patients requiring further assessment, supporting the feasibility of follow-up through telephone consultations. To further extend this approach, artificial intelligence-based follow-up systems may offer an opportunity to automate these interactions, reduce clinician workload, and streamline care pathways.
Objective: The aim of the study is to assess the clinical safety and effectiveness of an artificial intelligence-based follow-up call system (Dora-NL1) in identifying patients who require further assessment after cataract surgery in the Netherlands.
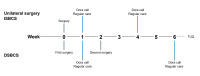
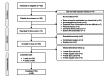
Methods: This prospective single-center study was conducted at the University Eye Clinic Maastricht, the Netherlands. Adult patients who underwent uncomplicated cataract surgery were eligible to participate. All patients received a Dora-NL1 follow-up telephone call at 1 and 4 weeks postoperatively in addition to standard care (a clinician-led telephone consultation at week 1 and an in-person hospital visit at week 4). The Dora-NL1 calls used a standard conversational flow to evaluate symptoms and recommend a clinical outcome. The recommended outcomes of Dora-NL1 were based on the symptoms reported by the patient. Clinical safety and accuracy were assessed by comparing Dora-NL1 outcomes to blinded clinician assessments of recorded calls and to standard postoperative care. Patient-reported usability was measured using the Telehealth Usability Questionnaire and Net Promoter Score.
Results: A total of 105 patients with a mean age of 72 (SD 7) years were included in the analysis. Dora-NL1 demonstrated high agreement with clinician-supervised calls, with symptom evaluation accuracy ranging from 89% to 99% (κ=0.390-0.947) and care management decision accuracy between 83% and 88% (κ=0.640-0.753). At week 1, Dora-NL1 showed a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 42% compared to standard clinician-led telephone consultations with no missed clinical concerns. At week 4, compared to the in-person follow-up, Dora-NL1 failed to identify 4 (4.1%) patients who required unexpected management changes, including 3 with asymptomatic complications detected only via slit lamp examination and 1 with complaints in the nonoperated eye. Patients rated Dora-NL1 positively, with Net Promoter Scores of +13.5 and +12.6 at week 1 and 4, respectively. The Telehealth Usability Questionnaire was completed by 98 patients, yielding a mean score of 3.19 (SD 1.13) on a 5-point scale, highlighting its simplicity, ease of use, and audibility.
Conclusions: Dora-NL1 is a safe and effective tool for automated postoperative screening following cataract surgery. It offers a safe alternative to clinician-led telephone consultations in routine cases but cannot fully replace in-person examinations.
Keywords: algorithm-based screening; digital health; eHealth intervention; postoperative follow-up; prospective clinical study; remote patient monitoring; telemedicine.
© Joukje C Wanten, Noël J C Bauer, Mohita Chowdhury, Aisling Higham, Nick de Pennington, Frank J H M van den Biggelaar, Rudy M M A Nuijts. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

