Optimize multi-objective transformation rules of water-sediment regulation for cascade reservoirs in the Lower Yellow River of China
- PMID: 40825810
- PMCID: PMC12361479
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15001-z
Optimize multi-objective transformation rules of water-sediment regulation for cascade reservoirs in the Lower Yellow River of China
Abstract
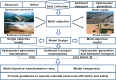
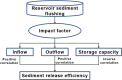
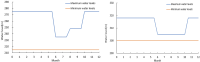
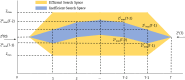
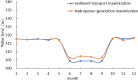
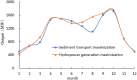
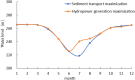
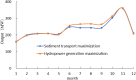
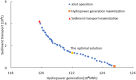
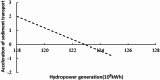
The Yellow River is characterized by water scarcity and high sediment load, leading to significant sedimentation issues in reservoirs. This severely restricts normal operation and contributes to frequent flooding, making it one of the most challenging problems in the Yellow River management. This study focuses on the operation of the Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi cascade reservoirs, developing a multi-objective model (hydropower generation and sediment transport) and two single-objective models (hydropower generation only and sediment transport only). An innovative method (ESS-NSGA-II) is proposed, combining Efficient Search Space (ESS) with the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) to optimize cascade reservoirs operation. We analyzed the impact and transformation rules of multiple objectives under various optimization schemes. The results indicate a non-linear competitive relationship between the hydropower generation and sediment transport. An extreme case indicates an increase of 0.49 billion kWh in hydropower generation (4.08% increase) leads to greatly reduce the amount of sediment transport (96.25% decrease), while still meeting both water supply and flood control. The findings also indicate that Xiaolangdi reservoir plays a dominant role in the operation of the two reservoirs. The impact of different schemes is mainly reflected in the variation in Xiaolangdi's discharge, with the sediment transport maximization scheme offering greater flood control potential. Furthermore, the efficiency of sediment transport is closely related to hydropower generation: when hydropower is below 12.28 billion kWh, the conversion efficiency from hydropower generation to sediment transport increases significantly. This research reveals the transformation rules between multi-objectives in cascade reservoir operation, providing a scientific basis for water and sediment regulation in the Yellow River Basin and offering valuable insights into prolonging reservoir lifespans.
Keywords: Efficient search space-non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (ESS- NSGA-II); Multi-objective optimization; The lower yellow river; Transformation rules; Water-sediment regulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Quantitative Analysis of the Influence of the Xiaolangdi Reservoir on Water and Sediment in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yellow River.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 28;20(5):4351. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20054351. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36901361 Free PMC article.
-
Scenario-based multi-objective optimization of reservoirs in silt-laden rivers: A case study in the Lower Yellow River.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Jul 10;829:154565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154565. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35307426
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Nguyen, B. Q. et al. Response of streamflow and sediment variability to cascade dam development and climate change in the Sai Gon dong Nai river basin. Clim. Dyn.62 (8), 7997–8017 (2024).
-
- Meng, Y. et al. Quantitative assessment of safety, society and economy, sustainability benefits from the combined use of reservoirs. J. Clean. Prod.324, 129242 (2021).
-
- Yan, M. et al. Optimizing reservoir operation considering downstream ecological demands of water quantity and fluctuation based on IHA parameters. J. Hydrol.600, 126647 (2021).
-
- Ren, S. et al. Sedimentation and its response to management strategies of the three Gorges reservoir, Yangtze river, China. Catena199, 105096 (2021).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

