Unraveling the Role of METTL3 in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis via m6A-CXCL1/NF-κB modulation
- PMID: 40825934
- PMCID: PMC12361391
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07841-4
Unraveling the Role of METTL3 in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis via m6A-CXCL1/NF-κB modulation
Abstract
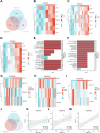
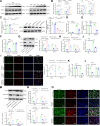
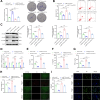
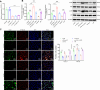
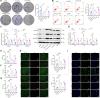
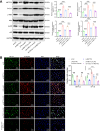
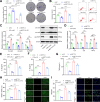
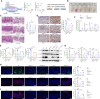
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a significant cause of gastric diseases, with its pathogenic mechanisms still not fully understood. This study investigates the role of METTL3, an enzyme involved in m6A methylation, in modulating the CXCL1/NF-κB signaling pathway in H. pylori-induced gastritis. Using both bioinformatics analysis of GEO database and experimental approaches including MeRIP, RIP assays, and immunostaining, this research highlights how METTL3 influences CXCL1 expression and NF-κB pathway activation. Results from both in vitro and in vivo models show that METTL3 increases inflammatory responses and apoptosis in gastric cells. Suppression of METTL3 resulted in decreased inflammation and apoptosis, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target in gastritis management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The author declares no competing interests. Ethical approval: All experiments involving mice were carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

