Targeting intestinal inflammation using locked nucleic acids delivered via lipid nanoparticles
- PMID: 40825982
- PMCID: PMC12361575
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63037-6
Targeting intestinal inflammation using locked nucleic acids delivered via lipid nanoparticles
Abstract
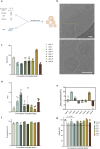
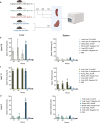
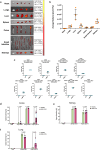
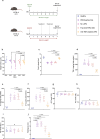
Locked nucleic acids are a third-generation antisense oligonucleotides with high binding affinity. A major limitation is the high dosages they require to achieve efficacy which may induce unwanted adverse effects. Here, we report the use of Lipid-based nanoparticles to deliver locked nucleic acids for treating intestinal inflammation in mice. Eight formulations with novel ionizable lipids were screened for stability and toxicity. Particles were loaded with splice-switcher sequence, enabling a precise assessment of potency in vitro. Three lead candidates were tested in vivo, demonstrating a 30-fold dose reduction compared to the unformulated oligonucleotides. The most potent formulation, encapsulating a sequence against Tumor necrosis factor alpha, was evaluated in a mouse model of colitis. Treatment reduced disease severity and inflammatory cytokines, with good safety. These findings support the use of lipid nanoparticles for the precise delivery of locked nucleic acids and highlight their promise for future therapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: D.P. receives licensing fees (to patents on which he was an inventor) from, invests in, and consults (or on scientific advisory boards or boards of directors) for lecturing (and received a fee), or conducts sponsored research at TAU for the following entities: ART Biosciences, BioNtech SE, Earli Inc., Kernal Biologics, LAND Therapeutics, Merck, Newphase Ltd., NeoVac Ltd., RiboX Therapeutics, Roche, SirTLabs Corporation, Teva Pharmaceuticals Inc. M.K., F.S., and K.G.L. are employees of Roche. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Koshkin, A. A. et al. LNA (locked nucleic acid): an RNA mimic forming exceedingly stable LNA:LNA duplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 13252–13253 (1998).
-
- Vester, B. & Wengel, J. LNA (locked nucleic acid): high-affinity targeting of complementary RNA and DNA. Biochemistry43, 13233–13241 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Braasch, D. A. & Corey, D. R. Novel antisense and peptide nucleic acid strategies for controlling gene expression. Biochemistry41, 4503–4510 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

