Adaptive deep SVM for detecting early heart disease among cardiac patients
- PMID: 40825995
- PMCID: PMC12361362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15938-1
Adaptive deep SVM for detecting early heart disease among cardiac patients
Abstract
Heart attack is one of the most common heart diseases, which causes more deaths worldwide. Early detection and continuous monitoring are essential in reducing the death rate caused by heart diseases. Machine learning gives a promising solution for early and accurate heart disease detection by analyzing the data from healthcare devices. Although existing studies have employed various machine learning techniques to detect heart disease, most of the techniques still face challenges in handling large healthcare datasets that affect the prediction outcomes. To solve this issue, the research work focuses on developing a novel framework for detecting heart disease in its early stages by using machine learning techniques. In the initial phase, the significant data required for the validation is collected from benchmark resources, and it is subjected to the weighted optimal features selection phase. Here, from the input data, the features are selected optimally and their weights are tuned using Enhanced Arbitrary Variable-based Ship Rescue Optimization (EAVSRO). Further, the optimally selected weighted features are fed into the detection phase. In this phase, an Adaptive Deep Support Vector Machine (AD-SVM) is employed to detect heart diseases. Once heart disease is detected, the Atrial Fibrillation (AF) rate is determined using the Adaptive Multiscale Convolution Capsule Network (AMCCNet). Finally, the AF rate is obtained from the developed AMCCNet, and its parameters are tuned using the same EAVSRO. Later, various experiments are performed in the recommended heart disease detection model over existing models to verify its effectiveness. The accuracy of the designed framework is 96.07%, which is enhanced than the other existing frameworks like CNN-LSTM, DCNN, Adaboost and SVM, respectively. Thus, the results proved that the developed model can effectively detect heart disease at the early stages and identify the AF rate, providing timely treatments.
Keywords: Adaptive deep support vector machine; Adaptive multiscale convolution capsule network; Atrial fibrillation rate identification; Enhanced arbitrary variable-based ship rescue optimization; Heart disease detection.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






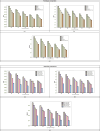
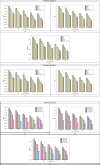

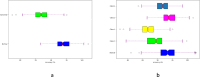
References
-
- Qadri, M., Raza, A., Munir, K. & Almutairi, M. S. Effective Feature Eng. Technique Heart Disease Prediction Mach. Learn. IEEE Access., 11, 56214–56224, (2023).
-
- Reshan, M. S. A. et al. Robust. Heart Disease Prediction Syst. Using Hybrid. Deep Neural Networks IEEE Access., 11, 121574–121591, (2023).
-
- Ramesh, Lakshmanna, K. & A Novel Early Detection and Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease Framework Using Hybrid Deep Learning Model. Neural Fuzzy Inference Syst. IEEE Access., 12, 26683–26695, (2024).
-
- Güven, M., Hardalaç, F., Özışık, K. & Tuna, F. Heart diseases diagnose via mobile application. Applied Sciences11 (5), 2430.Ozcan, Mert, and Serhat Peker, A classification and regression tree algorithm for heart disease modeling and prediction Healthcare Analytics, vol. 3, pp.100130, 2023. (2021).
-
- Baghdadi, N. A. et al. Advanced machine learning techniques for cardiovascular disease early detection and diagnosis. J. Big Data, 10(1), 144. (2023).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

