Usability and adoption in a randomized trial of GutGPT a GenAI tool for gastrointestinal bleeding
- PMID: 40825997
- PMCID: PMC12361555
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01896-5
Usability and adoption in a randomized trial of GutGPT a GenAI tool for gastrointestinal bleeding
Abstract
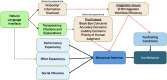
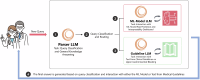
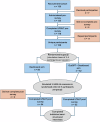
Generative AI (GenAI) may enhance clinical decision support systems (CDSS), but its impact on adoption remains unclear. We conducted a simulation-based randomized trial to evaluate whether a GenAI-enhanced CDSS, "GutGPT," improves adoption compared to an AI dashboard in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding management. Clinical trainees were randomized to either GutGPT or a comparator dashboard across three cases. The primary outcome was Behavioral Intention, from the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT). Secondary measures included additional constructs and decision accuracy. A total of 106 participants participated (52 GutGPT, 54 comparator). GutGPT users reported higher Effort Expectancy. Behavioral Intention had no significant difference. Qualitative analysis highlighted trust and workflow concerns. These findings suggest that usability alone is insufficient to drive adoption. As this study was conducted in a simulation without real-world integration or patient outcomes, further studies are needed. (Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov; Identifier: NCT05816473; Registered March 6, 2023).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Antioxidants for male subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD007411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007411.pub3. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 14;3:CD007411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007411.pub4. PMID: 25504418 Updated.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve hearing aid use in adult auditory rehabilitation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 18;2016(8):CD010342. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010342.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27537242 Free PMC article.
-
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori for prevention of aspirin-associated peptic ulcer bleeding in adults over 65 years: the HEAT RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Aug;29(42):1-62. doi: 10.3310/LLKF7871. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40844182 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lu, J. et al. Performance of multilabel machine learning models and risk stratification schemas for predicting stroke and bleeding risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Comput. Biol. Med150, 106126 (2022). - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

