Emerging biomarkers for early cancer detection and diagnosis: challenges, innovations, and clinical perspectives
- PMID: 40826140
- PMCID: PMC12359849
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-03003-6
Emerging biomarkers for early cancer detection and diagnosis: challenges, innovations, and clinical perspectives
Abstract
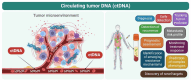
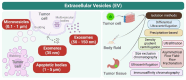
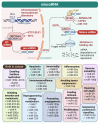
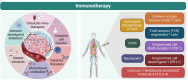
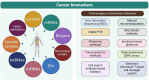
Early detection and accurate cancer diagnosis are crucial for improving patient outcomes and survival rates. This review presents a comprehensive and updated synthesis of emerging biomarkers, essential for providing non-invasive, efficient, and reliable methods to identify cancer in its early stages. An extensive literature review focuses on recent studies and advancements in both traditional and emerging biomarkers, including circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), exosomes, liquid biopsies, microRNAs (miRNAs), and immunotherapy biomarkers, which show promising potential for early cancer detection. Liquid biopsies, nanobiosensors, artificial intelligence, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are transforming biomarker discovery and application. Key challenges include low concentration and fragmentation, as well as clearance of ctDNA, the complexity of exosome isolation, inter-patient variability in miRNA expression, and the absence of clinical standardization. We also highlight the translational barriers in low-resource settings and suggest strategies for future implementation. We also underscore the limited diagnostic accessibility in low-resource settings, emphasizing the importance of equity in future applications. Future research should prioritize overcoming current challenges, promoting multidisciplinary collaboration, and creating standardized protocols to enhance the clinical utility of this approach.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Diagnosis; Exosomes; Expression; Immunotherapy; Liquid biopsy; MiRNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Prof. Dr. Javad Sharifi-Rad serves as an Associate Editor for European Journal of Medical Research. However, he was not involved in the peer-review or editorial decision-making process for this manuscript. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Institute NC. Cancer statistics 2024 [Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/statistics.
-
- Buchanan AH, Lennon AM, Rego SP, Choudhry OA, Elias PZ, Sadler JR, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of cancers diagnosed following detection by a blood-based multi-cancer early detection (MCED) test. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(16_suppl):3037.
-
- Isakova Dilnoza B, Farmankulova YR. Innovative Technologies in Early Diagnosis of Precancer and Cancer Diseases of the Cervix. J Med Genet Clin Biol. 2024;1(9):610.
-
- Adil S, Faiz M, Jawad A, Haseeb A, Muhammad A, Adnan A. The role of early diagnosis and intervention in improving outcomes for lung cancer. Innov Res Appl Biol Chem Sci. 2024;2(1):126–32.
-
- Garg P, Mohanty A, Ramisetty S, Kulkarni P, Horne D, Pisick E, et al. Artificial intelligence and allied subsets in early detection and preclusion of gynecological cancers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA). 2023;1878(6): 189026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

